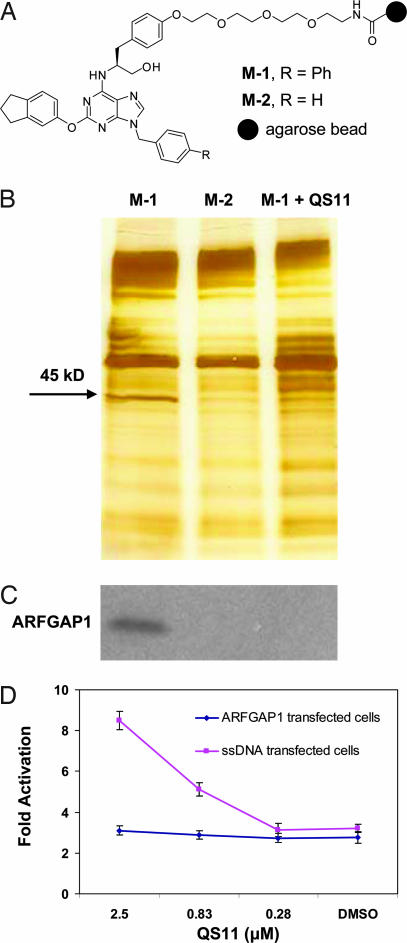
Fig. 2.
Affinity chromatography identified ARFGAP1 as the cellular target of QS11. (A) Chemical structures of affinity resins with QS11 (positive resin, M-1) or QS11-NC (negative resin, M-2) immobilized for target identification. (B) Pull-down experiments using the immobilized reagents M-1 [lane M-1, without soluble QS11; lane M-1 + QS11 (50 μM), with soluble QS11 at 50 μM] and M-2 (lane M-2). HEK293 cell lysates were incubated with the affinity matrices at 4°C for 1 h. Bound proteins were eluted, resolved on a 4–20% Tris-glycine gel, and visualized with silver staining. The band that contains ARFGAP1 is indicated by the arrow. (C) Western blot of ARFGAP1 resin-bound protein. Proteins that were resolved on a 4–20% Tris-glycine gel as in B were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and analyzed with an antibody against ARFGAP1. (D) Overexpression of ARFGAP1 cDNA blocks the synergistic effect of QS11 with Wnt-3a CM. HEK293 cells were transfected with Super(8X)TOPFlash reporter, pTK-RL plasmid, and ARFGAP1 cDNA (red line) or ssDNA (blue line) by using Fugene6. Cells were treated with QS11 at the indicated concentrations and Wnt-3a CM (1:1 vol/vol ratio to the growth medium) 24 h after transfection. Luciferase activities were measured 36 h after treatment with QS11 and Wnt-3a CM. The activation fold was normalized against renilla luciferase. Error bars are SD.