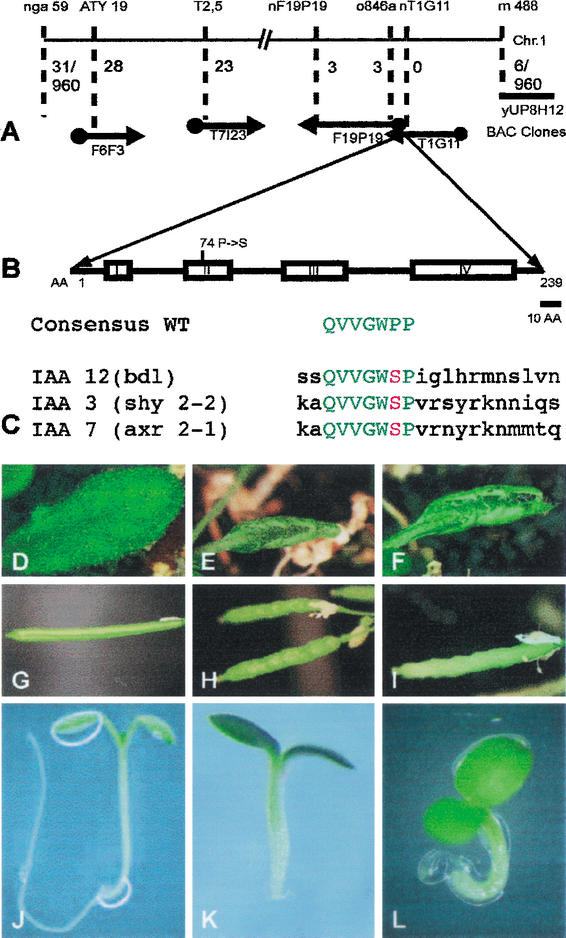
Figure 1.
Molecular identification of the BDL gene. (A) Molecular mapping. Molecular markers and BAC clones are shown at the top and bottom, respectively. Numbers indicate recombinants between markers and the BDL gene on BAC clone T1G11 (960 gametes tested). (B) BDL protein domain structure showing the four conserved domains of IAA proteins with the Pro 74 → Ser amino acid exchange in bdl mutant protein. (C) Homologous amino acid exchanges in the conserved domain II of IAA12 (bdl), IAA3 (shy2-2) and IAA7 (axr2-1) mutant proteins. The consensus sequence of wild-type is shown for comparison. (D–L) Phenotypic analysis of transgenic progeny from wild-type plants transformed with the bdl mutant genomic fragment. (D,G,J) Wild-type (BDL/BDL) control; (E,H,K) bdl heterozygous (E,H) and homozygous (K) mutant controls; (F,I,L) transgenic BDL/BDL with one (F,I) or two copies (L) of the bdl transgene. (D–F) Leaves, (G–I) siliques, (J–L) seedlings.