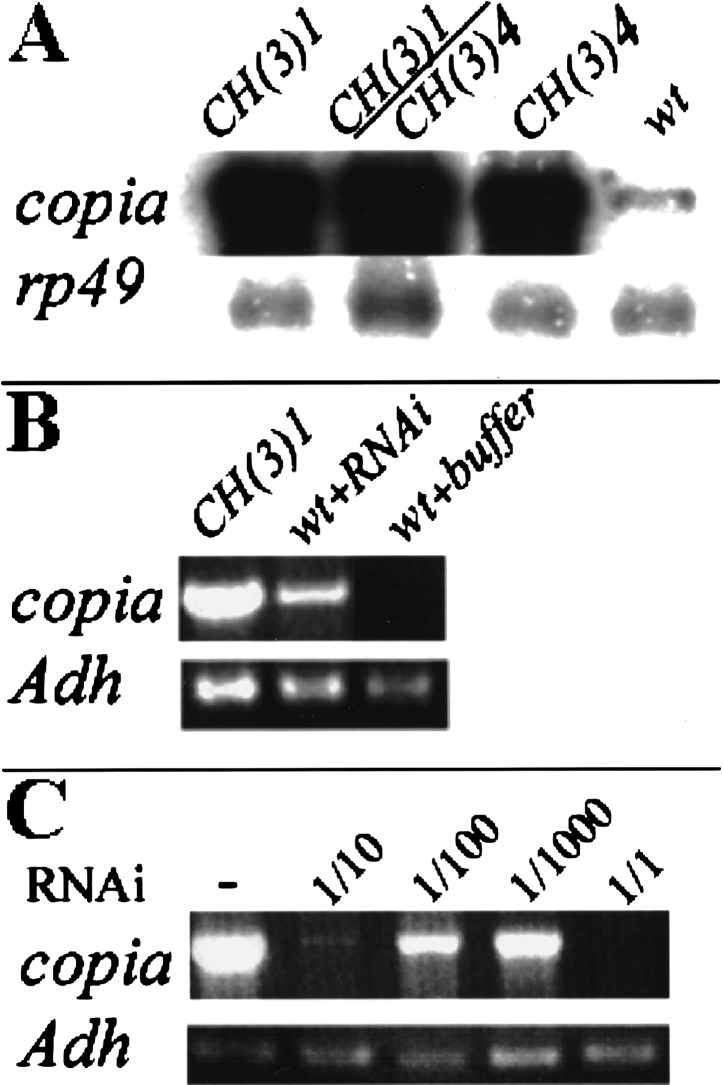
Figure 4.
Parp mutations or Parp (RNAi) elevate copia transcript levels. (A) A Northern blot of total RNA from second instar larvae of the indicated genotypes was probed with copia sequences. The 5.5-kb copia transcript is overproduced up to 50-fold in CH(3)1 or CH(3)4 homozygotes, and in CH(3)1/CH(3)4 trans-heterozygotes compared to wild-type. An rp49 probe was used as a loading control. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR shows that injection of Parp-specific RNAi, but not buffer, causes copia RNA to be overproduced. Primers specific to Adh served as a loading control. (C) Copia RNA accumulation does not cause lethality. Injection of mutant CH(3)1 embryos with RNAi specific to copia suppressed the accumulation of excess copia RNA and resulted in the elimination of all copia transcripts detectable by RT-PCR within 16 h. Sequential dilutions of the RNAi gave a graded response. However, the treatment did not rescue larval lethality.