Abstract
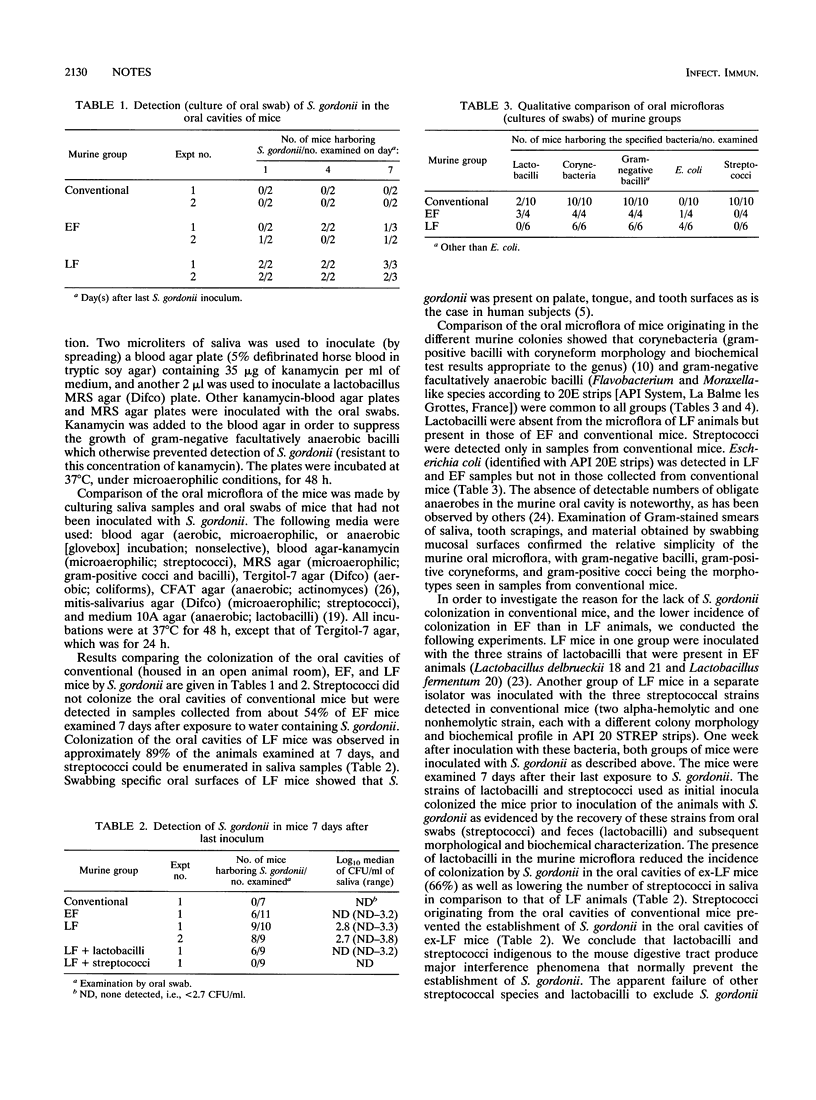
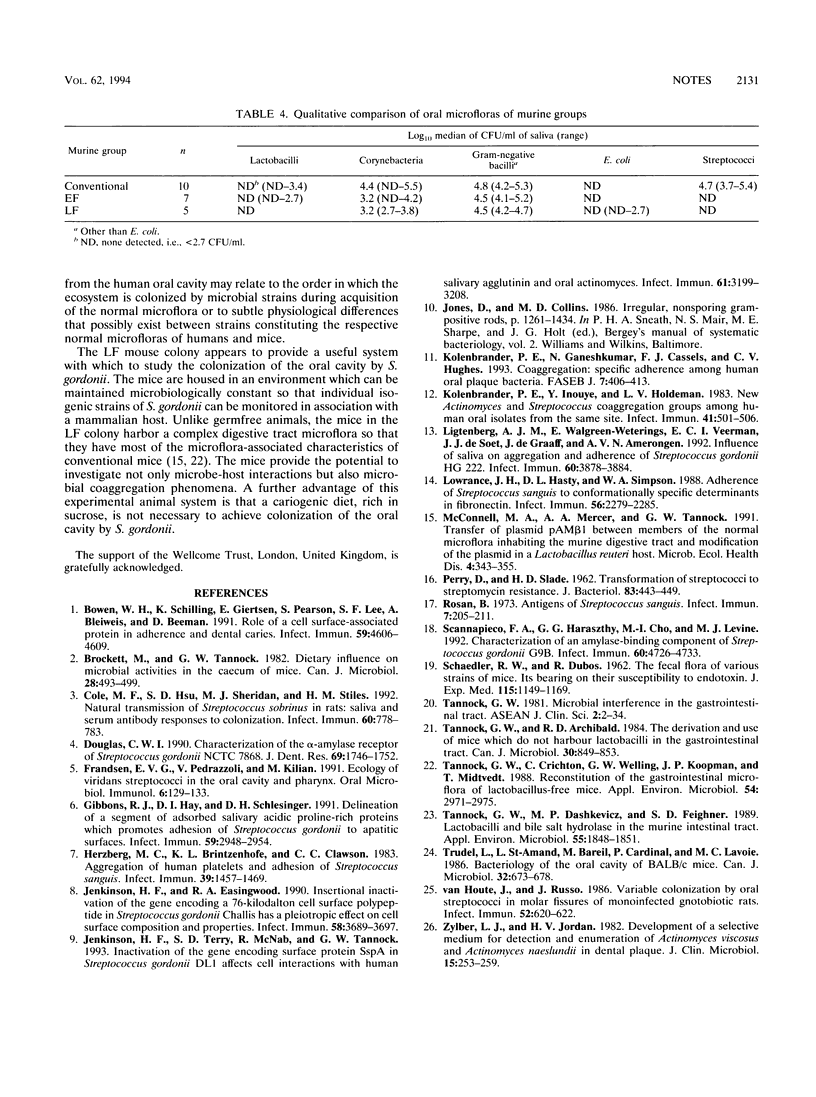
Streptococcus gordonii DL1 (Challis) colonized the oral cavities of BALB/c mice that lacked streptococci, enterococci, and lactobacilli (LF mice) as members of an otherwise complex digestive tract microflora. Conventional mice, in comparison, were refractory to colonization by S. gordonii. Mice that harbored lactobacilli but were free of streptococci and enterococci (EF mice) had a lower incidence of colonization by S. gordonii than LF animals. The LF mouse system should be useful in the study of the molecular mechanisms that enable S. gordonii to inhabit the oral cavity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen W. H., Schilling K., Giertsen E., Pearson S., Lee S. F., Bleiweis A., Beeman D. Role of a cell surface-associated protein in adherence and dental caries. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4606–4609. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4606-4609.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockett M., Tannock G. W. Dietary influence on microbial activities in the caecum of mice. Can J Microbiol. 1982 May;28(5):493–499. doi: 10.1139/m82-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. F., Hsu S. D., Sheridan M. J., Stiles H. M. Natural transmission of Streptococcus sobrinus in rats: saliva and serum antibody responses to colonization. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):778–783. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.778-783.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. W. Characterization of the alpha-amylase receptor of Streptococcus gordonii NCTC 7868. J Dent Res. 1990 Nov;69(11):1746–1752. doi: 10.1177/00220345900690110701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen E. V., Pedrazzoli V., Kilian M. Ecology of viridans streptococci in the oral cavity and pharynx. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Jun;6(3):129–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1991.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Hay D. I., Schlesinger D. H. Delineation of a segment of adsorbed salivary acidic proline-rich proteins which promotes adhesion of Streptococcus gordonii to apatitic surfaces. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2948–2954. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2948-2954.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg M. C., Brintzenhofe K. L., Clawson C. C. Aggregation of human platelets and adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1457–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1457-1469.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Easingwood R. A. Insertional inactivation of the gene encoding a 76-kilodalton cell surface polypeptide in Streptococcus gordonii Challis has a pleiotropic effect on cell surface composition and properties. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3689–3697. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3689-3697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Terry S. D., McNab R., Tannock G. W. Inactivation of the gene encoding surface protein SspA in Streptococcus gordonii DL1 affects cell interactions with human salivary agglutinin and oral actinomyces. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3199–3208. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3199-3208.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Ganeshkumar N., Cassels F. J., Hughes C. V. Coaggregation: specific adherence among human oral plaque bacteria. FASEB J. 1993 Mar;7(5):406–413. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.5.8462782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Inouye Y., Holdeman L. V. New Actinomyces and Streptococcus coaggregation groups among human oral isolates from the same site. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.501-506.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligtenberg A. J., Walgreen-Weterings E., Veerman E. C., de Soet J. J., de Graaff J., Amerongen A. V. Influence of saliva on aggregation and adherence of Streptococcus gordonii HG 222. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3878–3884. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3878-3884.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to conformationally specific determinants in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2279-2285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY D., SLADE H. D. Transformation of streptococci to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:443–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.443-449.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):205–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.205-211.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R. J. The fecal flora of various strains of mice. Its bearing on their susceptibility to endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1149–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scannapieco F. A., Haraszthy G. G., Cho M. I., Levine M. J. Characterization of an amylase-binding component of Streptococcus gordonii G9B. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4726–4733. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4726-4733.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Archibald R. D. The derivation and use of mice which do not harbour lactobacilli in the gastrointestinal tract. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jun;30(6):849–853. doi: 10.1139/m84-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Crichton C., Welling G. W., Koopman J. P., Midtvedt T. Reconstitution of the gastrointestinal microflora of lactobacillus-free mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2971–2975. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2971-2975.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Dashkevicz M. P., Feighner S. D. Lactobacilli and bile salt hydrolase in the murine intestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1848–1851. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1848-1851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel L., St-Amand L., Bareil M., Cardinal P., Lavoie M. C. Bacteriology of the oral cavity of BALB/c mice. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Aug;32(8):673–678. doi: 10.1139/m86-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber L. J., Jordan H. V. Development of a selective medium for detection and enumeration of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii in dental plaque. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):253–259. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.253-259.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Russo J. Variable colonization by oral streptococci in molar fissures of monoinfected gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):620–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.620-622.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


