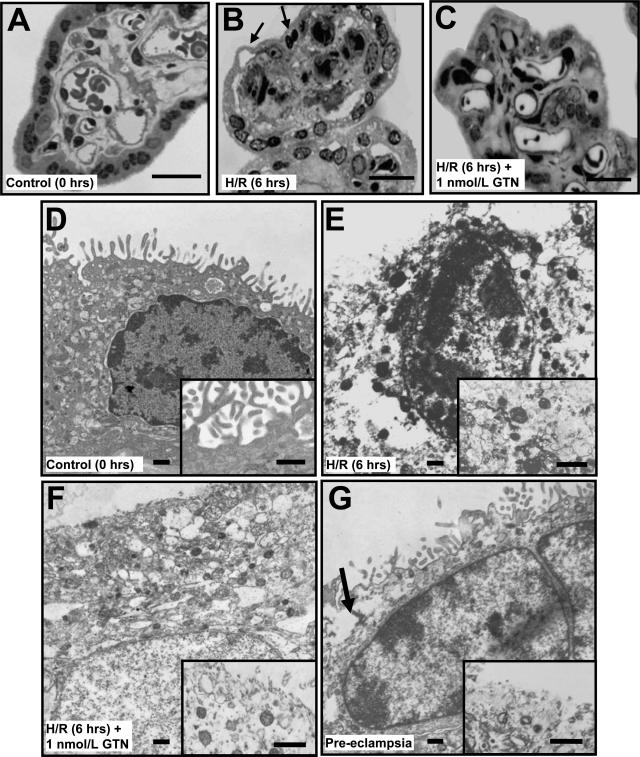
Figure 7.
Morphological analysis of chorionic villi at the light (A–C) and electron (D–G) microscopic levels. Villi were processed immediately after delivery (A, D); after 6 hours of H/R (B, E); and after 6 hours of H/R in the presence of GTN (1 nmol/L; C, F). G: An additional control consisted of villi from a preeclamptic pregnancy. Apoptotic changes such as the lifting of the syncytiotrophoblast layer and the presence of picnotic nuclei (B, arrows) were more evident in untreated explants after H/R than in explants treated with GTN (C, F) or fresh placental tissues (A, D). D: Ultrastructural analysis revealed an intact syncytial membrane with abundant microvilli in villi from uncomplicated pregnancies fixed immediately after delivery (inset). E: After H/R the syncytial nuclei often appeared small and with extensive chromatin condensation. E, inset: The presence of cytoplasmic vacuolization and loss of syncytial membrane integrity were also evident in explants after H/R. F: Treatment with GTN during the exposure to H/R resulted in a higher number of well-preserved syncytial nuclei and greater continuity of the cytoplasmic membrane (inset). Compared with explants fixed immediately after delivery, the number of microvilli in tissues treated with GTN during exposure to H/R was reduced (inset). Villi from a preeclamptic pregnancy exhibited some of the morphological features as villi exposed to H/R, such as disruption of the syncytiotrophoblast membrane (G, arrow; inset). Scale bars: 25 μm (A–C); 0.5 μm (D–G).