Figure 1. Characterization of immunity.
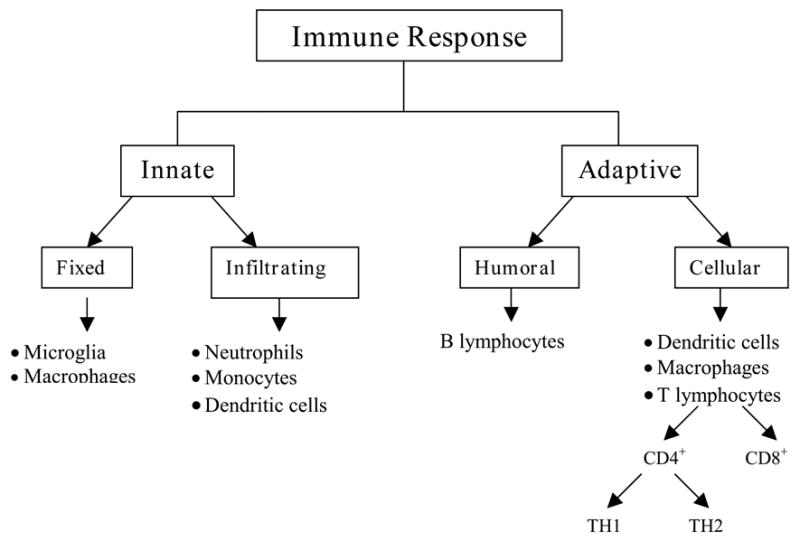
In general, cells associated with innate immunity are either tissue specific or derived from a circulating pool of inflammatory cells. The adaptive response consists of both humoral and cellular components. The humoral response is typified by the production of antibodies and is mediated by B-lymphocytes. The cellular response is mediated by T-lymphocytes, which are further classified into cytotoxic, CD8+ and helper cells, CD4+. CD4+ cells give rise to either TH1 or TH2 types of responses. TH1 cells produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, TNF-agr;, and IL-6, whereas TH2 cells secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-4, IL-10 and TGF-β. Abbreviations: Interferon-gamma - IFN-γ; tumor necrosis factor-alpha - TNF-agr;; interleukin-6 - IL-6; interleukin-4 - IL-4; interleukin-10 - IL-10; and transforming growth factor-beta - TGF-β.
