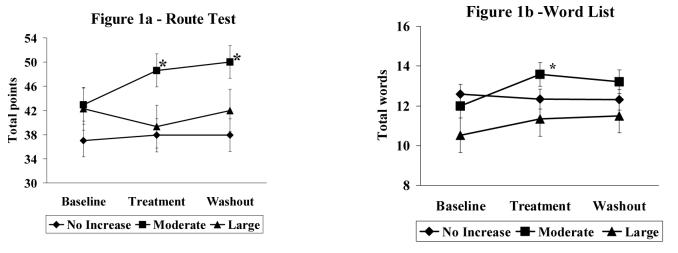
Figure 1a.
Mean total points correct on the Route Test, a measure of spatial and navigational memory. Figure 1b. Mean total points correct on Word List recall, a measure of verbal memory. Diamond represents men who demonstrated no change in serum T (0-10 nmol/L) during treatment. Square represents men who demonstrated a moderate increase in serum T (11-50 nmol/L) during treatment. Triangle represents men who demonstrated a large increase in serum T (> 50 nmol/L) during treatment. Error bars represent standard error of measurement. Men with a moderate increase in serum T levels evidenced a significant improvement on the Route test during treatment and at washout compared to baseline (*p<.05) and compared to men who had no increase or a large increase in serum T levels (*p<.05) (1a). Men with a moderate increase in serum T levels during treatment also demonstrated a significant improvement on the Word List test compared to baseline (*p<.05) (1b). There was no significant change from baseline for Route Test or Word list in the no or large increase groups.