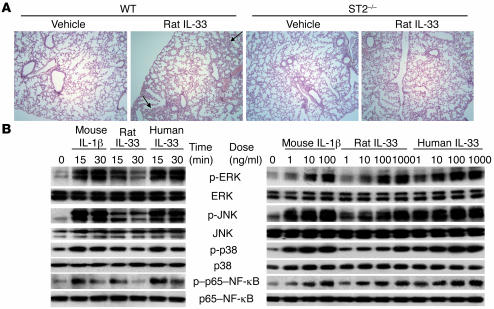
Figure 7. Rat IL-33 has weaker potency than human IL-33 and causes focal pulmonary inflammation in mice.
(A) Representative specimens of lung (H&E stain; original magnification, ×100) from mice 1 week after sham operation with or without 7 days’ treatment with rat IL-33 (2 μg/d). In the pulmonary parenchyma of WT mice, IL-33 treatment led to mild focal infiltrations of inflammatory cells (arrows) within and adjacent to vessels. This was not seen in vehicle-treated mice. These changes were not observed in ST2–/– mice with or without IL-33 treatment. (B) Time- and dose-dependent activation of ERK, JNK, p38, and p65–NF-κB by mouse IL-1β and recombinant mature rat or human IL-33 are shown. Mature rat IL-33 showed relatively weaker activation of MAPKs and NF-κB than the other proteins.