Abstract
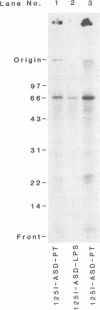
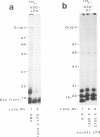
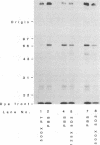
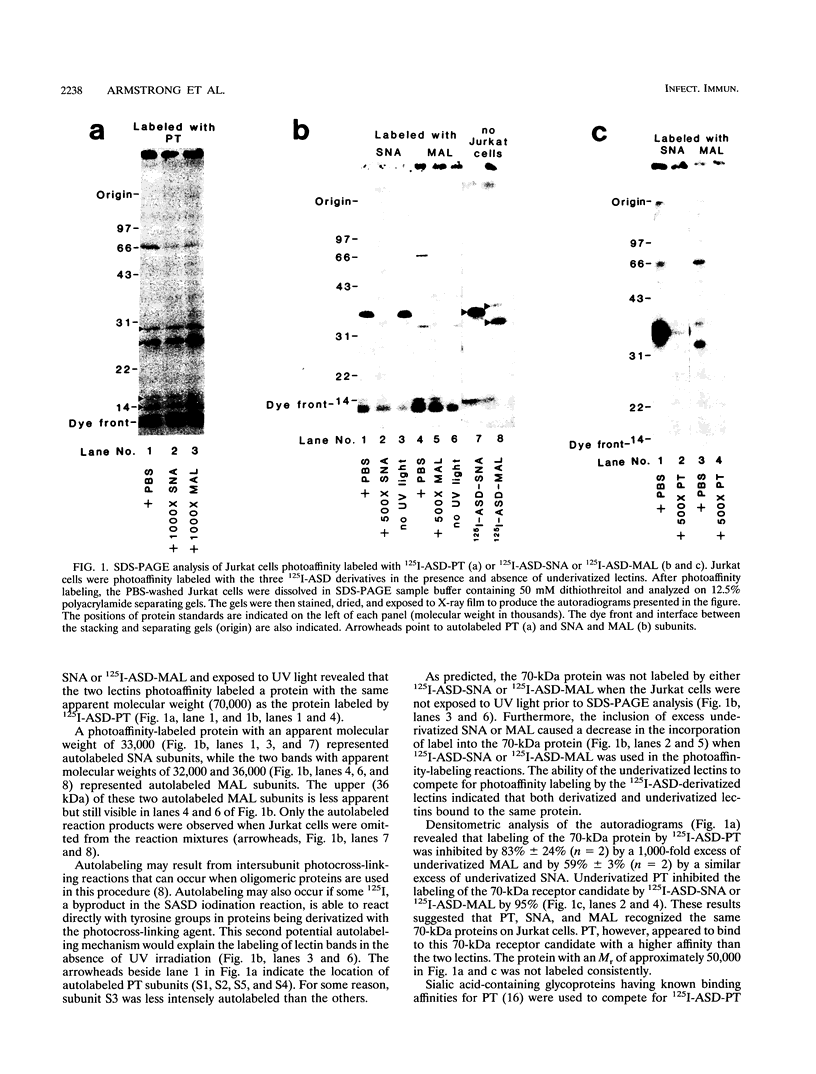
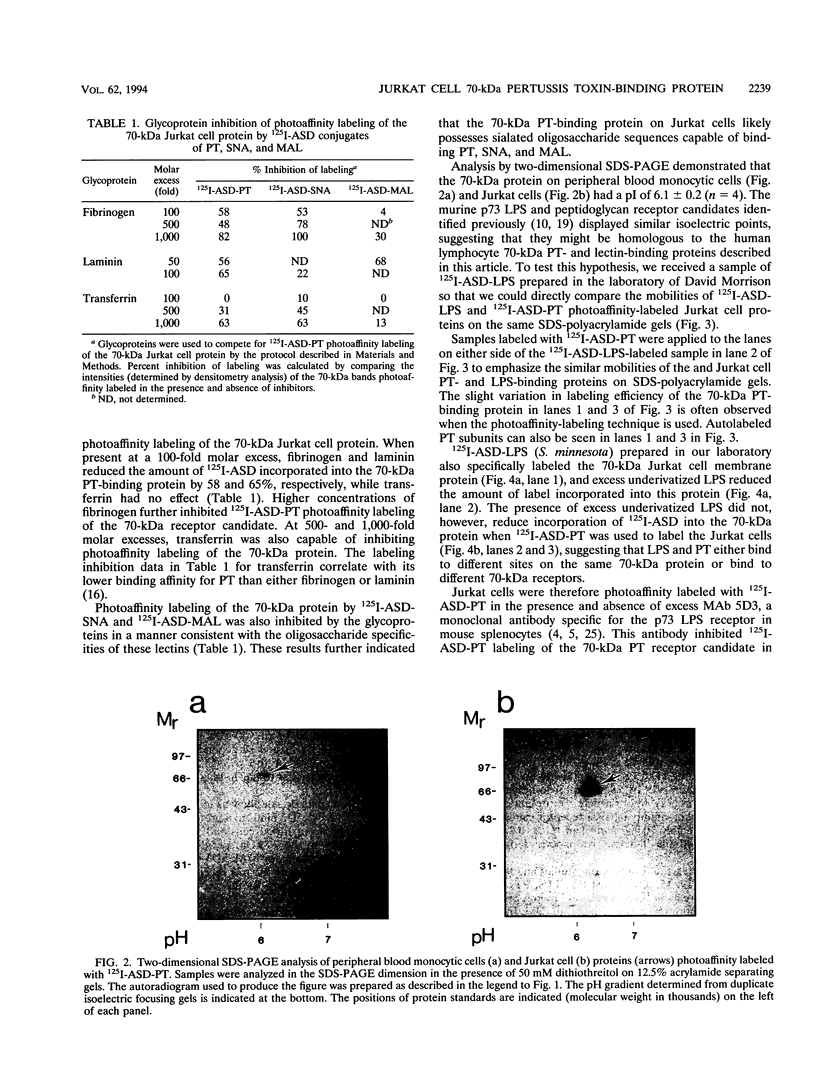
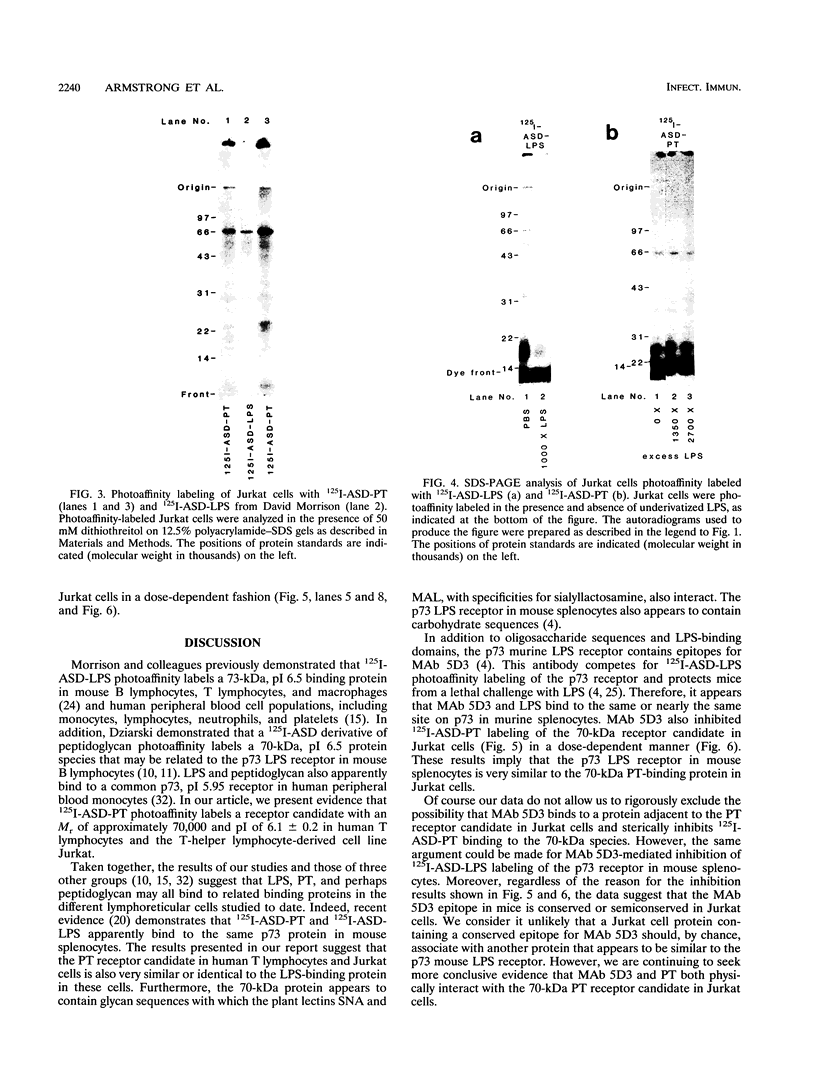
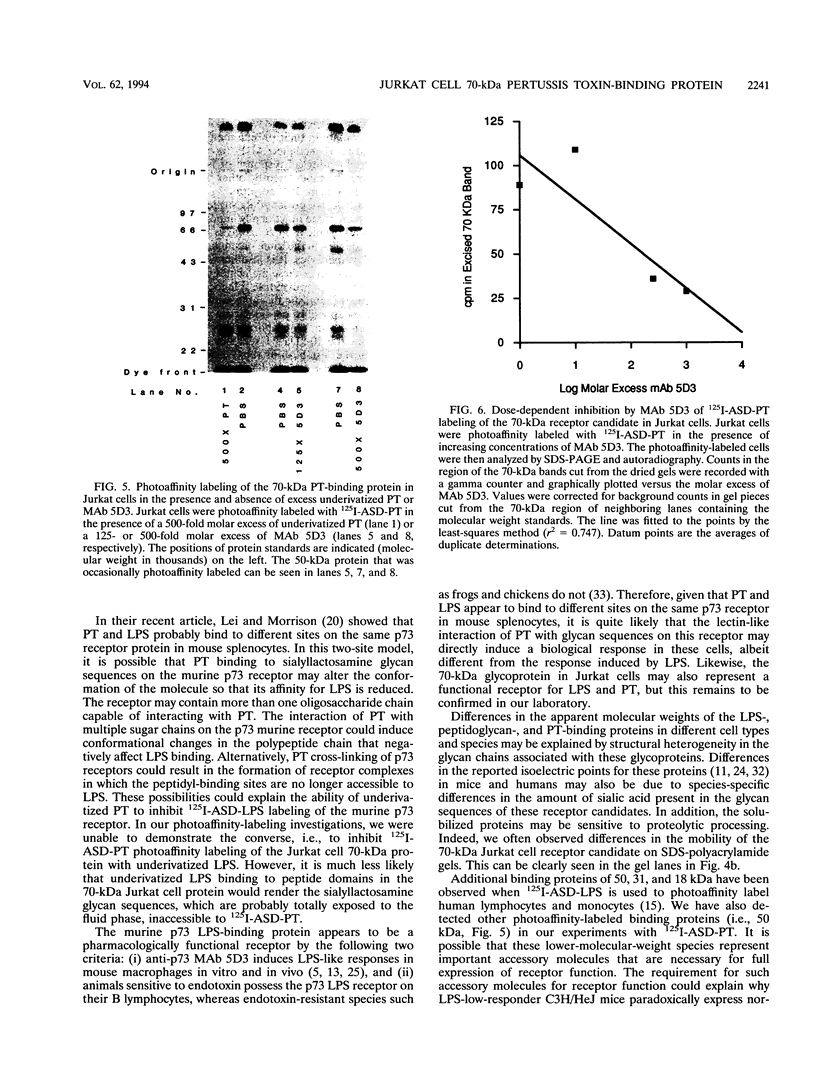
125I-ASD photoaffinity-labeling derivatives of pertussis toxin (125I-ASD-PT) or lipopolysaccharide (125I-ASD-LPS) labeled similar 70-kDa proteins in Jurkat cells, a cell line derived from human CD4+ T lymphocytes. Labeling of this 70-kDa protein by 125I-ASD-PT was inhibited by underivatized PT but not by underivatized LPS. However, an immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody with specificity for the p73 LPS receptor in murine splenocytes (S. W. Bright, T.-Y. Chen, L. M. Flebbe, M.-G. Lei, and D. C. Morrison, J. Immunol. 145:1-7, 1990) inhibited 125I-ASD-PT labeling of the 70-kDa species in Jurkat cells. Our results suggested that PT may bind to the same 70-kDa protein as LPS does in Jurkat cells but that PT and LPS bind to different sites on this receptor candidate. 125I-ASD-PT photoaffinity labeling of the 70-kDa protein was also inhibited by underivatized glycoproteins to which PT has been shown to bind, and this inhibition correlated with the relative binding affinities of the glycoproteins for PT. 125I-ASD derivatives of two sialic acid-specific plant lectins, Maackia amurensis leukoagglutinin and Sambucus nigra agglutinin, with oligosaccharide binding specificities similar to those of PT also labeled a 70-kDa protein in Jurkat cells. This suggests that the 70-kDa PT receptor candidate in Jurkat cells likely contains sialooligosaccharide sequences to which PT, M. amurensis leukoagglutinin, and S. nigra agglutinin bind. The cross-reacting epitope recognized by monoclonal antibody 5D3 in this 70-kDa species might overlap the PT- and LPS-binding sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong G. D., Howard L. A., Peppler M. S. Use of glycosyltransferases to restore pertussis toxin receptor activity to asialoagalactofetuin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8677–8684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. D., Peppler M. S. Maintenance of biological activity of pertussis toxin radioiodinated while bound to fetuin-agarose. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1294–1299. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1294-1299.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., David J. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Lectin-like binding of pertussis toxin to a 165-kilodalton Chinese hamster ovary cell glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4895–4899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright S. W., Chen T. Y., Flebbe L. M., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Generation and characterization of hamster-mouse hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies with specificity for lipopolysaccharide receptor. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Bright S. W., Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Morrison D. C. Induction of macrophage-mediated tumor cytotoxicity by a hamster monoclonal antibody with specificity for lipopolysaccharide receptor. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Klein M. Single-step purification of pertussis toxin and its subunits by heat-treated fetuin-sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;67(7):387–391. doi: 10.1139/o89-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Armstrong G. D. Lymphocyte receptors for pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3840–3846. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3840-3846.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Demonstration of peptidoglycan-binding sites on lymphocytes and macrophages by photoaffinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4713–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide bind to the same binding site on lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4719–4725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. S., Huber K. S., Gray M. C., Hewlett E. L., Engelhard V. H. Pertussis toxin effects on T lymphocytes are mediated through CD3 and not by pertussis toxin catalyzed modification of a G protein. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Chen T. Y., Crawford R. M., Nacy C. A., Morrison D. C., Meltzer M. S. Cytotoxic activity and production of toxic nitrogen oxides by macrophages treated with IFN-gamma and monoclonal antibodies against the 73-kDa lipopolysaccharide receptor. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2069–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier-Brossette N., Bourget I., Breittmayer J. P., Ferrua B., Fehlmann M., Cousin J. L. Pertussis toxin-induced mitogenesis in human T lymphocytes. Immunopharmacology. 1991 Mar-Apr;21(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling J. L., Hamill D. R., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Identification and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on human peripheral blood cell populations. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):845–852. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.845-852.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heerze L. D., Armstrong G. D. Comparison of the lectin-like activity of pertussis toxin with two plant lectins that have differential specificities for alpha (2-6) and alpha (2-3)-linked sialic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1224–1229. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91579-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons L. I., MacLennan A. P. Isolation of the lymphocytosis promoting factor-haemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 29;580(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., June C. H., Grosmaire L. S., Rabinovitch P. S. Crosslinking of surface antigens causes mobilization of intracellular ionized calcium in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1384–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Flebbe L., Roeder D., Morrison D. C. Identification and characterization of lipopolysaccharide receptor molecules on mammalian lymphoid cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;256:445–466. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-5140-6_41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Evidence that lipopolysaccharide and pertussis toxin bind to different domains on the same p73 receptor on murine splenocytes. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1359–1364. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1359-1364.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with S2 subunit of pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1488–1493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Stimpson S. A., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding receptors on murine splenocytes. III. Binding specificity and characterization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1925–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Silverstein R., Bright S. W., Chen T. Y., Flebbe L. M., Lei M. G. Monoclonal antibody to mouse lipopolysaccharide receptor protects mice against the lethal effects of endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1063–1068. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C. The case for specific lipopolysaccharide receptors expressed on mammalian cells. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Peacock M. G. Action of pertussigen (pertussis toxin) on serum IgE and on Fc epsilon receptors on lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1990 May;127(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90136-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Peacock M. G. Role of pertussigen (pertussis toxin) on the mouse protective activity of vaccines made from Bordetella species. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(4):341–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera P. Y., Chan T. Y., Morrison D. C., Vogel S. N. Detection and analysis of the 80-kd lipopolysaccharide receptor in macrophages derived from Lpsn and Lpsd mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 May;51(5):501–506. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.5.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin R. L., Bieber M. M., Teng N. N. Lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan share binding sites on human peripheral blood monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):135–142. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder D. J., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Endotoxic-lipopolysaccharide-specific binding proteins on lymphoid cells of various animal species: association with endotoxin susceptibility. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1054-1058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. S., Corey S. J., Rosoff P. M. Identification of a 43-kilodalton human T lymphocyte membrane protein as a receptor for pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):678–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y. Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: correlation of specific antibodies against two antigens, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin with mouse protectivity in an intracerebral or aerosol challenge system. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.415-421.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Masure H. R., Tuomanen E. I. Pertussis toxin has eukaryotic-like carbohydrate recognition domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya N., Goldstein I. J., Broekaert W. F., Nsimba-Lubaki M., Peeters B., Peumans W. J. Fractionation of sialylated oligosaccharides, glycopeptides, and glycoproteins on immobilized elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) bark lectin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Apr;254(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. E., Boodhoo A., Armstrong G. D., Cockle S. A., Klein M. H., Read R. J. The crystal structure of pertussis toxin. Structure. 1994 Jan 15;2(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Prpic V., Johns J. A., Powers F. S., Graber S. E., Forbes J. T., Exton J. H. Bacterial toxins affect early events of T lymphocyte activation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):234–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI113865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad C. F., Carchman R. A. Human T lymphocyte mitogenesis in response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin is associated with an early elevation in cytosolic calcium concentrations. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom R. E., Casnellie J. E. Pertussis toxin activates protein kinase C and a tyrosine protein kinase in the human T cell line Jurkat. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Braun D., Larson G., Hansson G. C., Hill R. Receptor analogs and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):267–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell G. J., Peppler M. S., Bonnah R. A., Clark C. G., Chong P., Armstrong G. D. Lectinlike properties of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1854–1857. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1854-1857.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. C., Cummings R. D. The immobilized leukoagglutinin from the seeds of Maackia amurensis binds with high affinity to complex-type Asn-linked oligosaccharides containing terminal sialic acid-linked alpha-2,3 to penultimate galactose residues. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4576–4585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witvliet M. H., Burns D. L., Brennan M. J., Poolman J. T., Manclark C. R. Binding of pertussis toxin to eucaryotic cells and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3324–3330. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3324-3330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witvliet M. H., Vogel M. L., Wiertz E. J., Poolman J. T. Interaction of pertussis toxin with human T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5085–5090. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5085-5090.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Morrison D. C. Synthesis and biochemical characterization of a photoactivatable, iodinatable, cleavable bacterial lipopolysaccharide derivative. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15068–15074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Wout J., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Rozdzinski E., Wright S. D., Tuomanen E. I. Role of carbohydrate recognition domains of pertussis toxin in adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3303–3308. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3303-3308.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]