Abstract
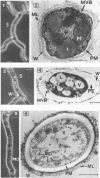
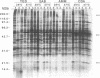
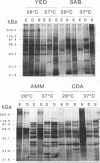
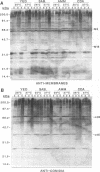
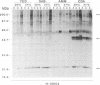
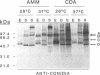
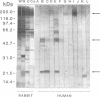
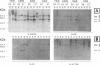
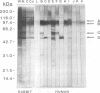
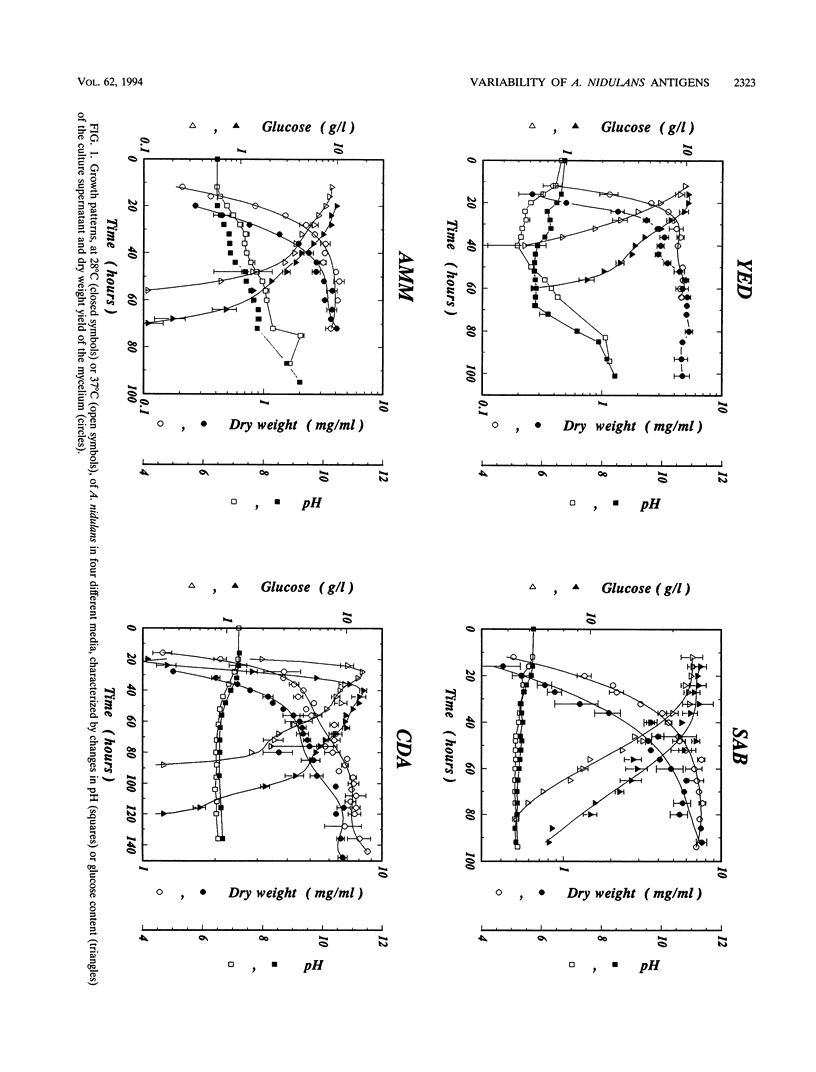
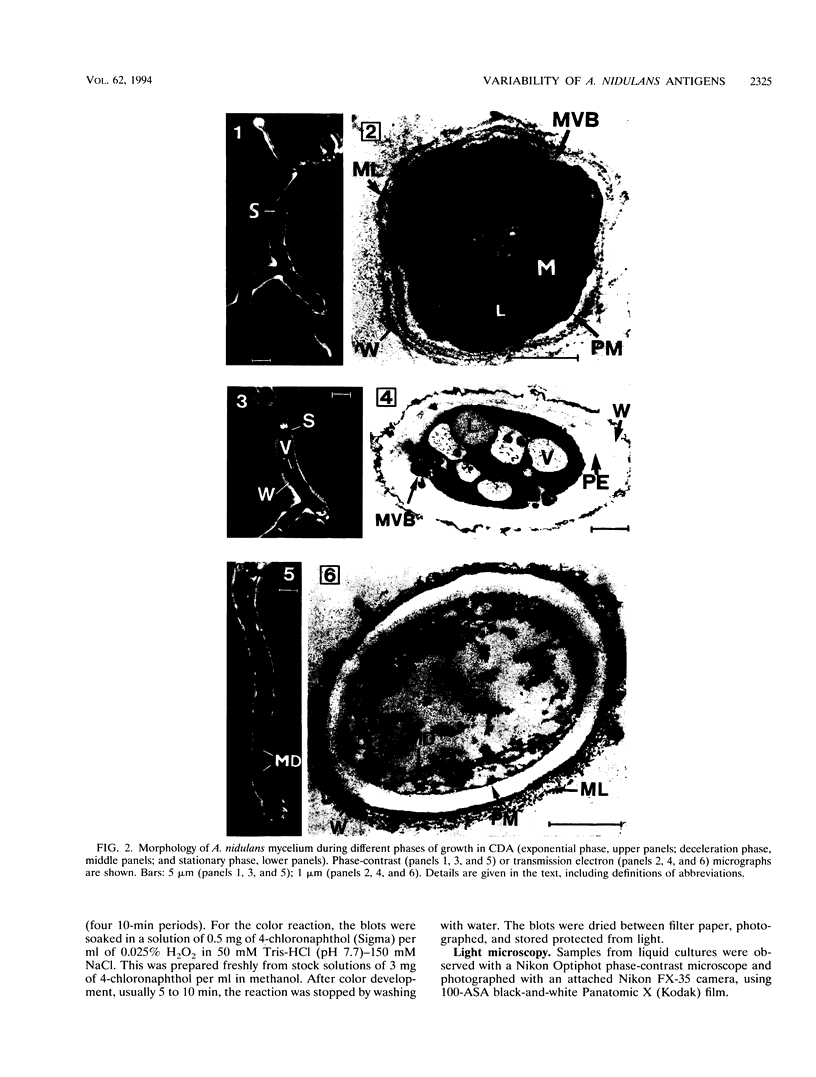
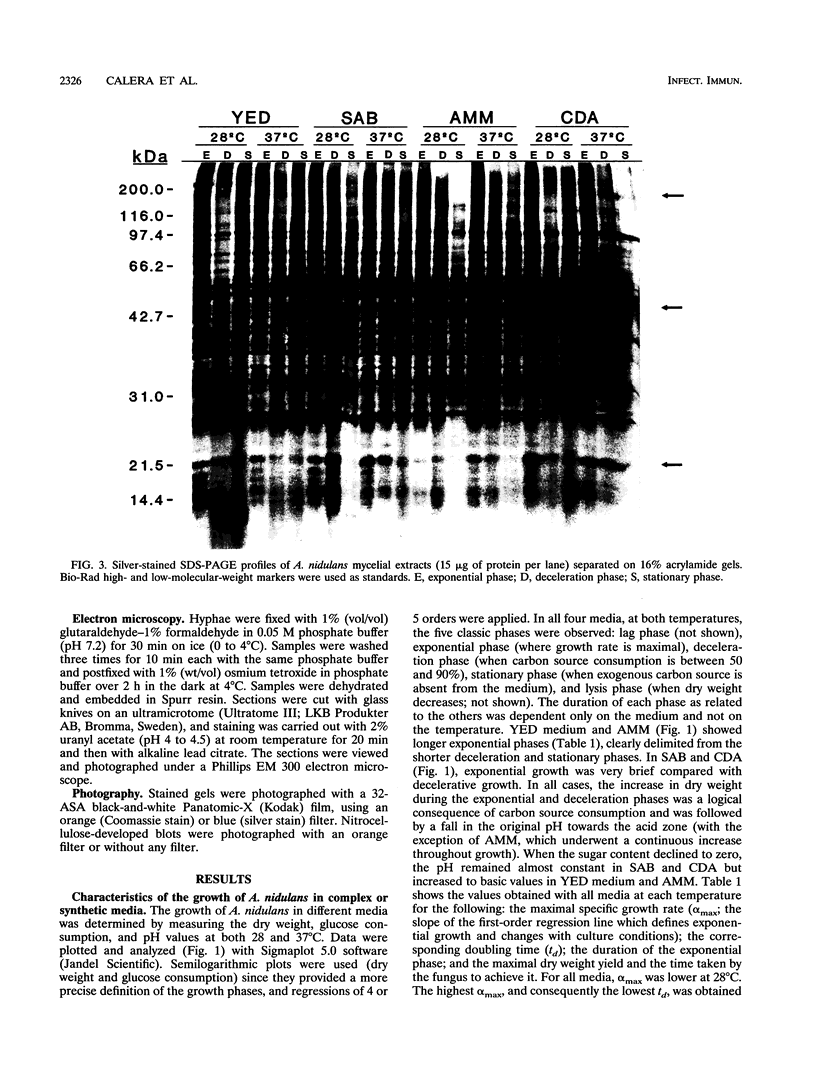
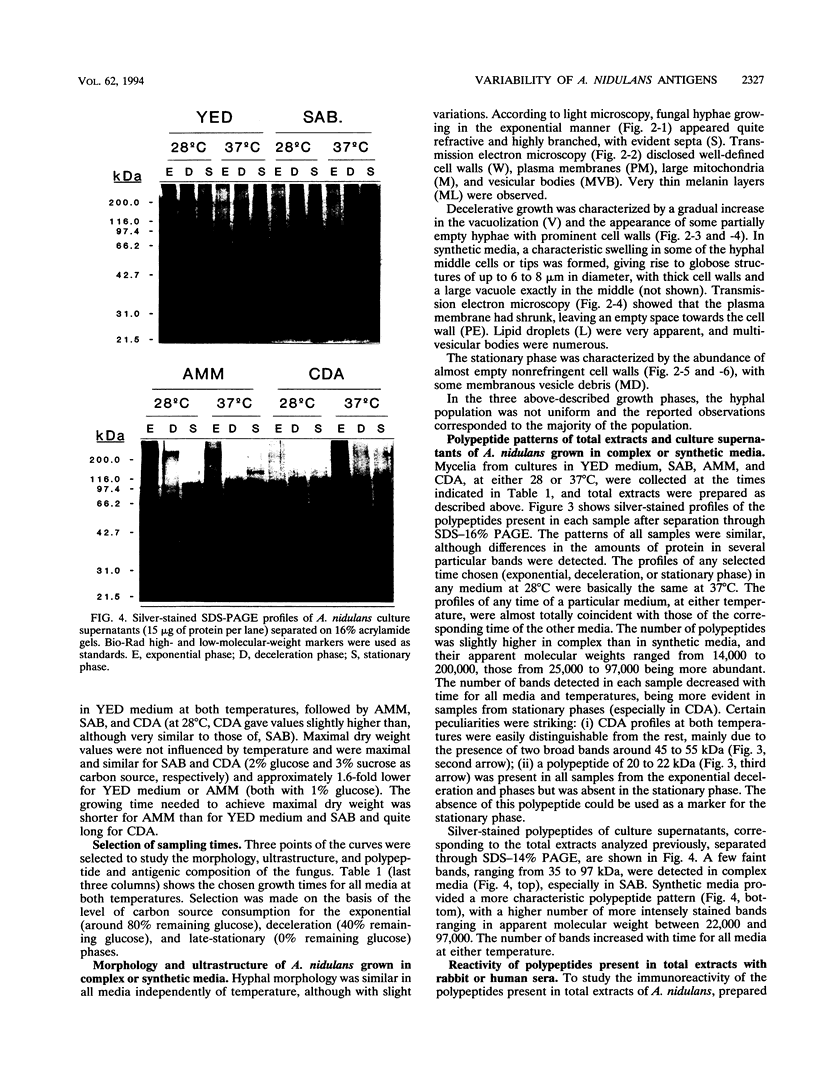
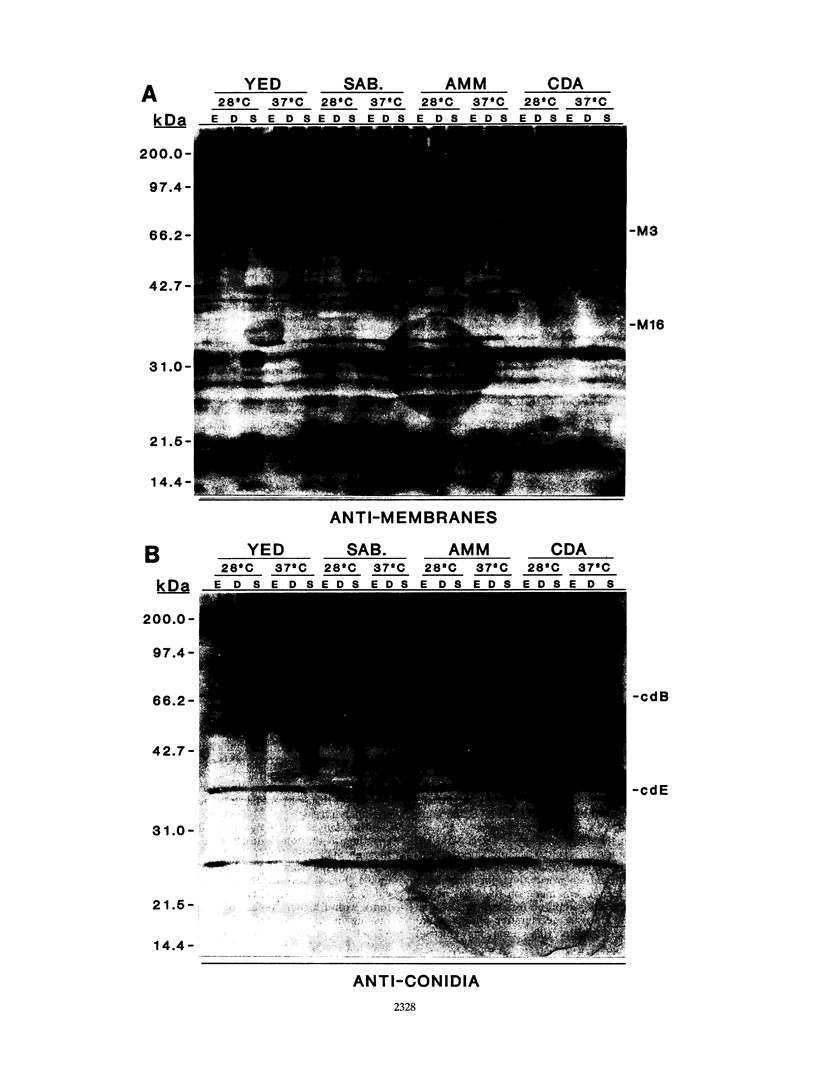
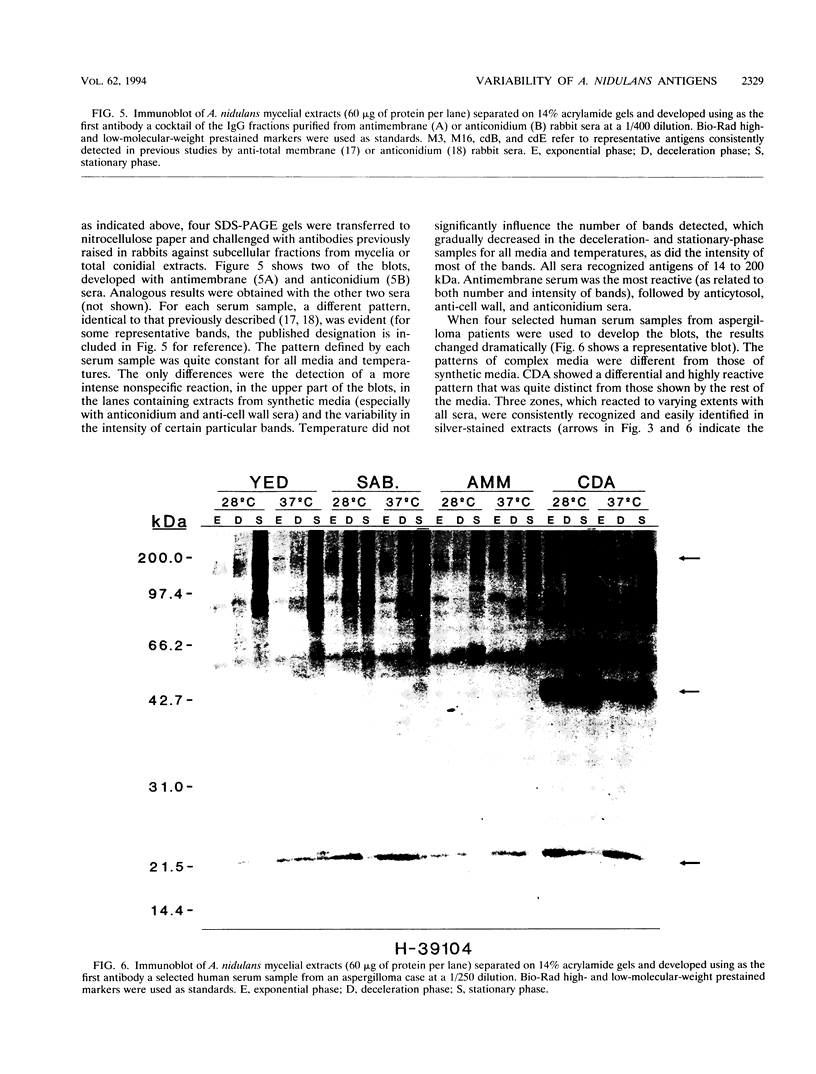
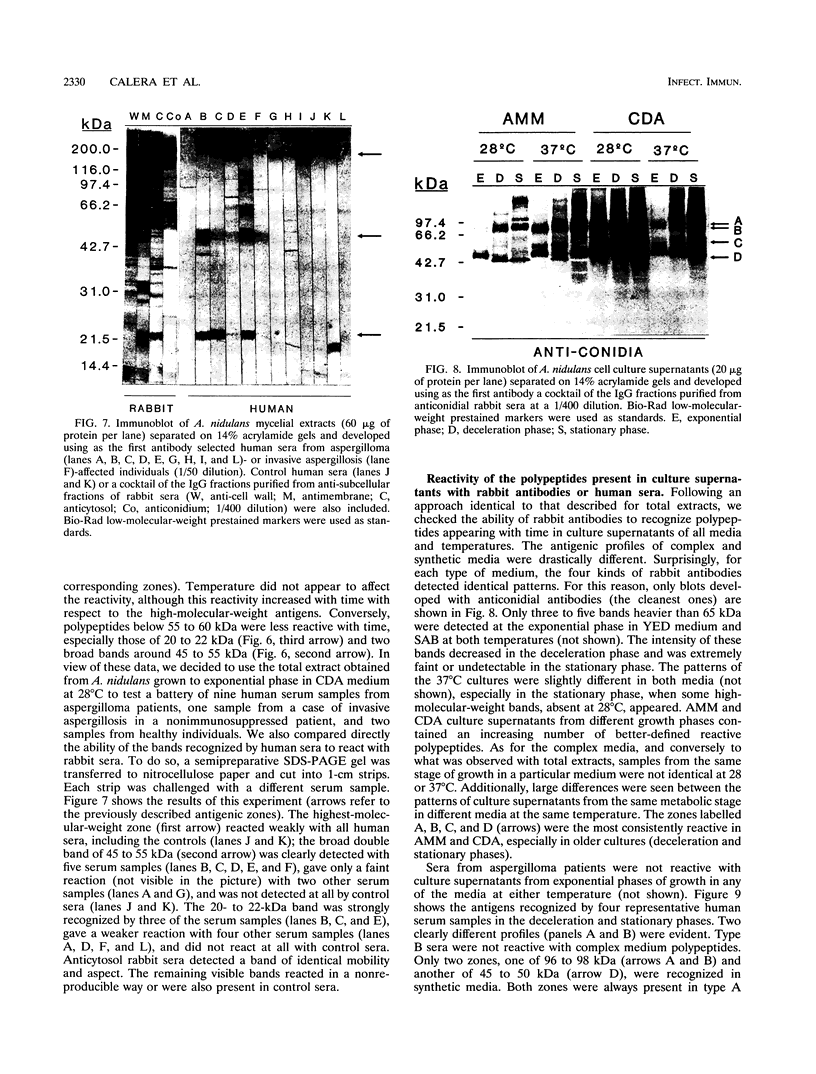
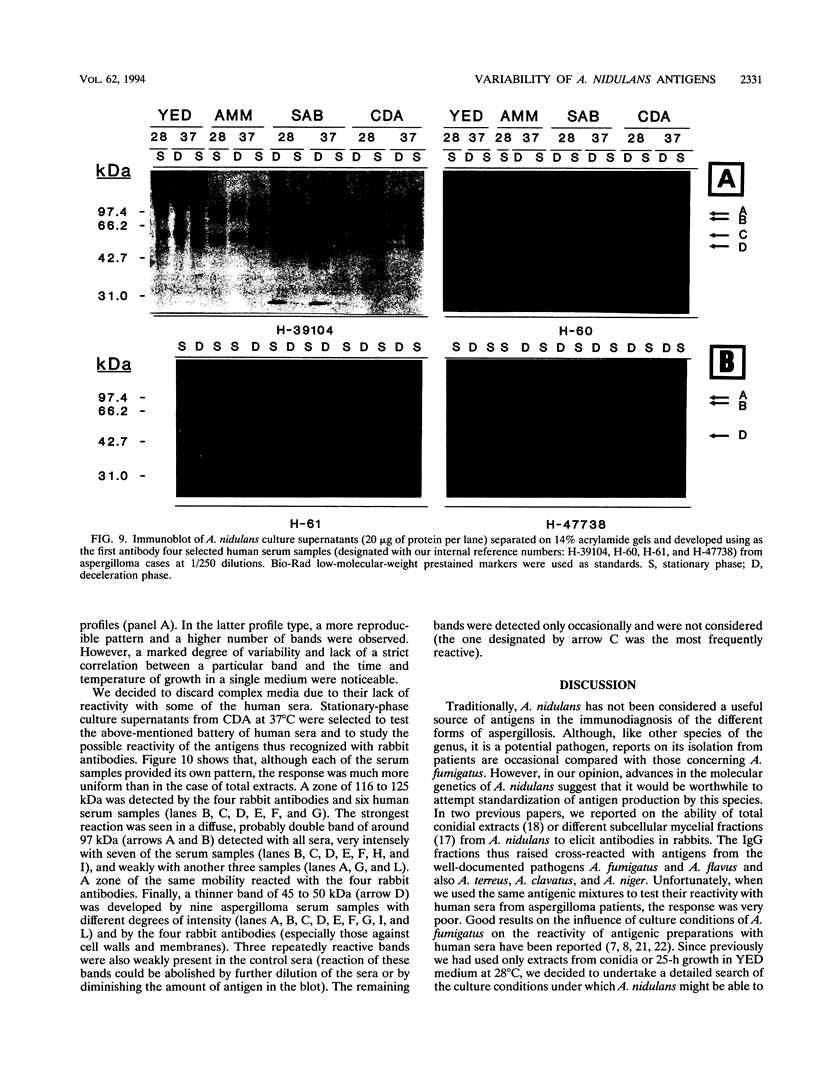
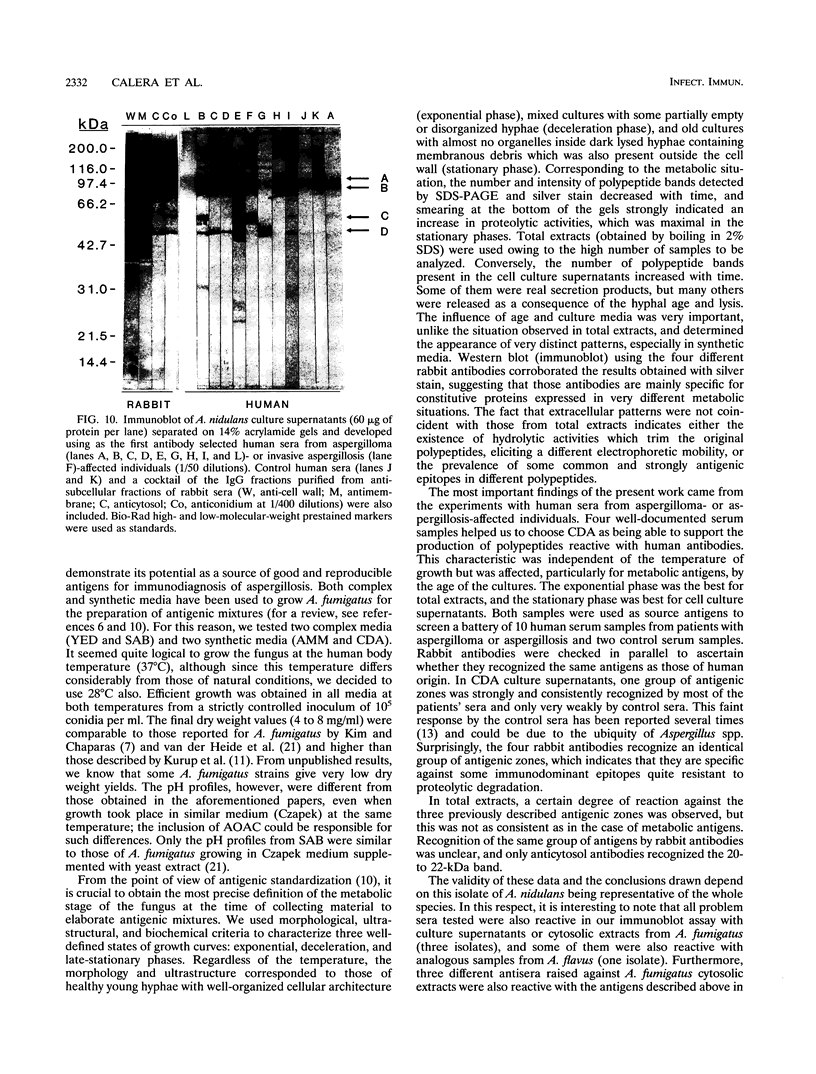
The influence of culture medium and time and temperature of growth on the appearance of Aspergillus nidulans antigens was determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by silver staining or Western blot (immunoblot), of the proteins present in total cellular extracts or culture supernatants. Samples in the exponential, deceleration, and stationary growth phases were selected by biochemical, morphological, and ultrastructural criteria. Protein and antigen patterns (detected with rabbit antibodies) from total extracts were very similar in all cases, and the major differences observed seemed to depend on the age of the cultures. Culture supernatant patterns were highly dependent on the type of medium (complex or defined) and the age of the culture. Temperature did not significantly influence these results. The reproducible reactivity of selected human sera from aspergilloma-affected individuals was strictly associated with the use of defined media, especially Czapek Dox-AOAC, in both total extracts and culture supernatants. Extended growth times were necessary in the case of metabolic antigens (those obtained from culture supernatants). Screening of a battery of 10 selected human serum samples from patients with aspergilloma or invasive aspergillosis demonstrated that two of the antigens (96 to 98 and 45 kDa) from stationary-phase culture supernatants in Czapek Dox-AOAC medium were consistently reactive. When considered together as one unit, both antigens reacted with more than 50% of the sera, and at least one or the other of the antigens reacted with more than 90% of the sera. Less consistent results were obtained for two somatic antigens (from total cell extracts) of 45 to 50 and 20 to 22 kDa.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruda L. K., Platts-Mills T. A., Fox J. W., Chapman M. D. Aspergillus fumigatus allergen I, a major IgE-binding protein, is a member of the mitogillin family of cytotoxins. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1529–1532. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvanico N. J., Du Pont B. L., Huang C. J., Patterson R., Fink J. N., Kurup V. P. Antigens of aspergillus fumigatus. 1. Purification of a cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera of patients with aspergillus-related disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Sep;45(3):662–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Huber M., Kim S. J., Bennett J. E. Galactomannan antigenemia and antigenuria in aspergillosis: studies in patients and experimentally infected rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and characterization of an immunodominant 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus recognized by sera of patients with invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.309-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico P. M., Long W. K., Buckley H. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to a 58-kilodalton antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):316–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.316-322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn V. M. Antigenicity of Aspergillus species. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30(1):11–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Chaparas S. D. Characterization of antigens from Aspergillus fumigatus. I. Preparation of antigens from organisms grown in completely synthetic medium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Sep;118(3):547–551. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.3.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N., Scribner G. H., Falk M. J. Antigenic variability of Aspergillus fumigatus strains. Microbios. 1977;19(77-78):191–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., John K. V., Resnick A., Fink J. N. A partially purified glycoprotein antigen from Aspergillus fumigatus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(3):263–269. doi: 10.1159/000233984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Kumar A. Immunodiagnosis of aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Oct;4(4):439–456. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.4.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Ramasamy M., Greenberger P. A., Fink J. N. Isolation and characterization of a relevant Aspergillus fumigatus antigen with IgG- and IgE-binding activity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;86(2):176–182. doi: 10.1159/000234568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latgé J. P., Moutaouakil M., Debeaupuis J. P., Bouchara J. P., Haynes K., Prévost M. C. The 18-kilodalton antigen secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2586–2594. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2586-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechura J. E., Huang C. J., Cohen S. H., Kidd J. M., Kurup V. P., Calvanico N. J. Antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Electrophoretic and clinical studies. Immunology. 1983 Aug;49(4):657–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puente P., Fernández N., Ovejero M. C., Leal F. Immunogenic potential of Aspergillus nidulans subcellular fractions and their polypeptide components. Mycoses. 1992 Sep-Oct;35(9-10):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1992.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puente P., Ovejero M. C., Fernández N., Leal F. Analysis of Aspergillus nidulans conidial antigens and their prevalence in other Aspergillus species. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4478–4485. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4478-4485.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem J., Meulemans L., Van Gerven F., Stynen D. Detection of circulating galactomannan by Pastorex Aspergillus in experimental invasive aspergillosis. Mycoses. 1990 Feb;33(2):61–69. doi: 10.1111/myc.1990.33.2.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide S., Kauffman H. F., de Vries K. Cultivation of fungi in synthetic and semi-synthetic liquid medium. I. Growth characteristics of the fungi and biochemical properties of the isolated antigenic material. Allergy. 1985 Nov;40(8):586–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide S., Kauffman H. F., de Vries K. Cultivation of fungi in synthetic and semi-synthetic liquid medium. II. Immunochemical properties of the antigenic and allergenic extracts. Allergy. 1985 Nov;40(8):592–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]