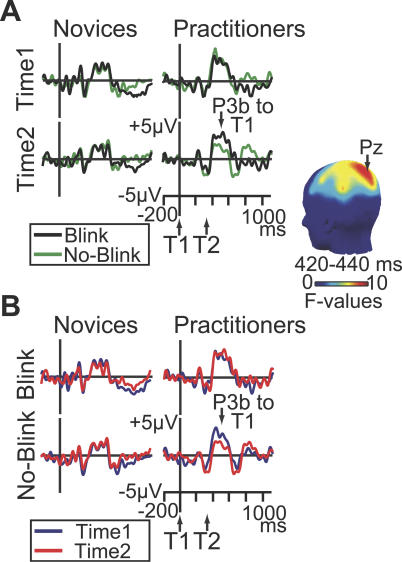
Figure 3. Effects of Intensive Mental Training on Brain-Resource Allocation to T1.
(A) Brain potentials from electrode Pz, time-locked to T1 onset on short-interval trials as a function of T2 accuracy (no-blink vs. blink), session, and group. These data show that, as hypothesized, the practitioners showed a significantly greater reduction in T1-elicited P3b amplitude than the novices in no-blink versus blink trials at time 2 versus time 1. The scalp map shows electrode sites where this three-way interaction was significant between 420 and 440 ms.
(B) Brain potentials from electrode Pz, time-locked to T1 onset on short-interval trials as a function of session, T2 accuracy, and group. This figure panel illustrates that intensive mental training was associated with a selective reduction in T1-elicited P3b amplitude in no-blink trials in the practitioner group.