Figure 3.
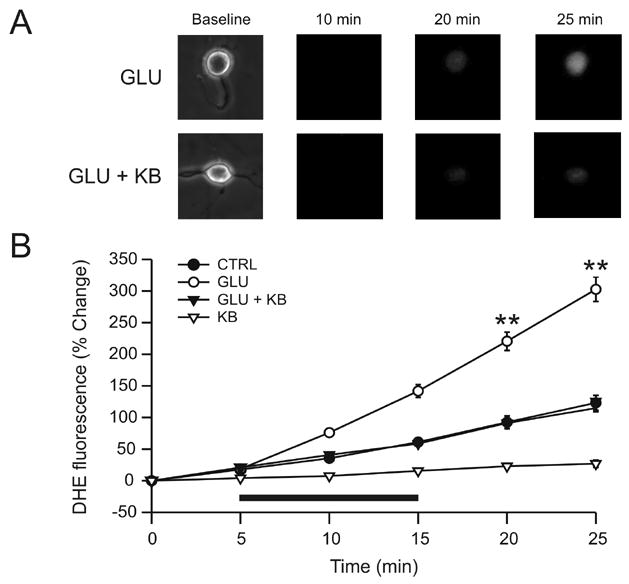
Ketones (KB) block glutamate-induced increases in superoxide radicals. (A) Exposure of neurons to glutamate (GLU; 10 μM) for 10 min led to a time-dependent increase in the fluorescence of DHE, a marker for the free radical superoxide (n = 15). In the presence of both GLU and KB (D-β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, 1 mM each), the increase in DHE fluorescence was smaller (GLU + KB; n = 16). (B) GLU (horizontal bar) provoked a time-dependent increase in DHE fluorescence that persisted after discontinuation of GLU but that was significantly reduced (p = 0.01) by KB, down to levels similar to the control group (CTRL; n = 11). The application of KB alone (KB; n = 8) significantly decreased the DHE signal below that of control experiments (p = 0.04). ** p < 0.01.
