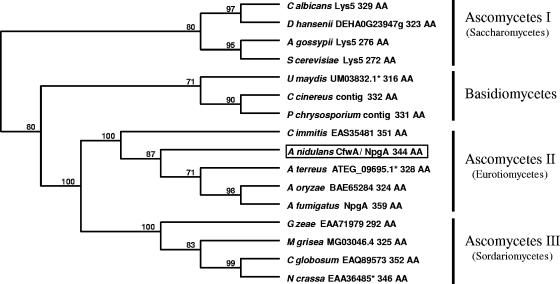
FIG. 3.
Many fungi contain a single orthologous PPTase. Indicated PPTases were aligned with ClustalW. The phylogenetic tree was generated with the distance-based unweighted-pair group method using average linkages using MacVector 7.2. Numbers at the nodes indicate percentages of 2,000 bootstrap replicates in which the node was recovered. Sequences are identified by species name, followed by protein name or GenBank accession number and protein size. Coprinus cinereus (C cinereus) and Phanerochaete chrysosporium (P chrysosporium) proteins were manually deduced from contigs AACS01000118 (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard [http://www.broad.mit.edu]) and AADS01000639 (DOE Joint Genome Institute [http://genome.jgi-psf.org/whiterot1/whiterot1.home.html]), respectively. Asterisks indicate proteins that seem to have been incorrectly annotated and were manually deduced as follows: only the last 316 and 328 amino acids (AA) of Ustilago maydis (U maydis) UM03832.1 and Aspergillus terreus (A terreus) ATEG_09695.1 were considered to be CfwA/NpgA homologues, respectively. Neurospora crassa (N crassa) EAAA36485 is missing the first exon and is incorrectly annotated as being a protein of only 284 amino acids. Abbreviations for other organism names are as follows: C albicans, Candida albicans; D hansenii, Debaryomyces hansenii; A gossypii, Ashbya gossypii; S cerevisiae, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; C immitis, Coccidioides immitis; A oryzae, Aspergillus oryzae; A fumigatus, Aspergillus fumigatus; G zeae, Gibberella zeae; M grisea, Magnaporthe grisea; C globosum, Chaetomium globosum.