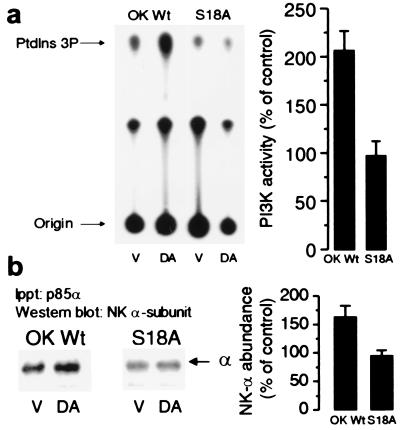
Figure 1.
Effect of Na+,K+-ATPase α subunit phosphorylation on the ability of DA to increase PI3K activity. (a) OK cells expressing the wild-type rat Na+,K+-ATPase α1 subunit or this isoform carrying the S18A mutation were incubated in the presence or absence of 1 μM DA for 2.5 min at 23°C. PI3K activity was determined in immunoprecipitates (equal amounts of precipitated material as assessed by Western blotting were used in each condition) with a polyclonal antibody raised against the p85α subunit whose epitope corresponds to the amino acids 333–430 within the N-terminal SH2 domain (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). (b) The presence of Na+,K+-ATPase α1 subunit in the immunoprecipitates was determined by Western blotting with a monoclonal antibody against the Na+,K+-ATPase α subunit. Experiments in a and b were repeated three and five times, respectively. Basal expression was similar in OK-Wt and S18A mutants as evidenced by Western blotting and Na+,K+-ATPase activity [Rb+ transport (nmol of Rb per mg of protein per min): OK-Wt, 9.8 ± 0.7 vs. S18A, 9.7 ± 1.0; hydrolytic activity in isolated membranes (μmol of Pi per mg of protein per min): OK-Wt, 0.305 ± 0.02 vs. S18A, 0.293 ± 0.01].