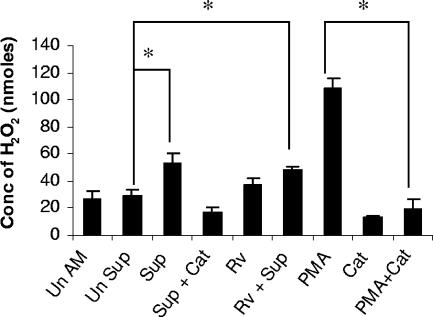
FIG. 4.
Production of hydrogen peroxide by alveolar macrophages treated with supernatants from infected neutrophils. Alveolar macrophages (2 × 105/well) were treated with supernatants from neutrophils infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI of 5) for 24 h (Sup), and H2O2 production was measured by using horseradish peroxide-dependent oxidation of phenol red. Alveolar macrophages treated with supernatants from uninfected neutrophils were used as controls (Un Sup). Some of the alveolar macrophages were treated with anti-recombinant guinea pig TNF-α antibody (1:600 dilution; data not shown). PMA and catalase (Cat) were used by macrophages as a stimulant and an inhibitor of H2O2 production, respectively. The other controls used were uninfected, untreated macrophages (Un AM); macrophages infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv at an MOI of 0.1 (Rv); and alveolar macrophages treated with supernatants from infected neutrophils and also infected with M. tuberculosis at an MOI of 0.1 (Rv + Sup). H2O2 concentrations (Conc) were expressed in nanomoles. The levels of production of H2O2 by different treatment groups (three animals per group) were compared with that by the untreated control by using ANOVA followed by Duncan's post hoc analysis. *, P < 0.05.