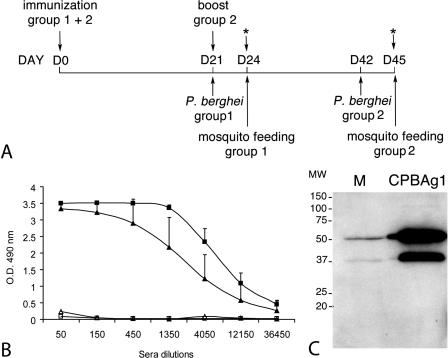
FIG. 5.
Mouse immunization with recombinant CPBAg1. (A) Immunization protocol. Mice in group 1 and group 2 were immunized with recombinant CPBAg1 protein on day 0. Mice in group 1 (eight immunized and eight control mice) were inoculated with P. berghei on day 21 and were used for mosquito feeding and ELISA experiments on day 24. Mice in group 2 (three immunized and three control mice) were given a booster on day 21, inoculated with P. berghei on day 42, and used for mosquito feeding and ELISA experiments on day 45. The blood (100 μl per mouse) for the ELISA experiments was collected after mosquito feeding. (B) CPBAg1-specific ELISA titers in sera from immunized and control mice. The titer of specific antibodies against CPBAg1 was measured in duplicate for each mouse 3 weeks after the first (group 1) and the booster (group 2) immunization. For each group, the average optical density reading at 490 nm was plotted against the reciprocal serum dilution. ▴ and ▪, antibody titers in sera from group 1 and 2 immunized mice, respectively; ▵ and □, antibody titers in sera from group 1 and 2 control mice, respectively. Endpoints were defined as the highest dilution yielding an absorbance reading at 490 nm greater than 0.5. The error bars represent standard deviations of the mean antibody titers for all mice within a group. (C) Analysis of antibody recognition of mosquito midgut proteins. M, 10 μg of protein from sugar-fed mosquito midgut; CPBAg1, 10 ng of CPBAg1 recombinant protein. The blot was probed with either serum from CPBAg1-immunized mice or pooled serum from control mice at a dilution of 1:200. The serum from CPBAg1-immunized mice, unlike the pool of serum from control mice (data not shown), specifically recognizes two bands corresponding to the zymogen (48.2-kDa) and mature (37-kDa) forms of CPBAg1 protein in mosquito midguts.