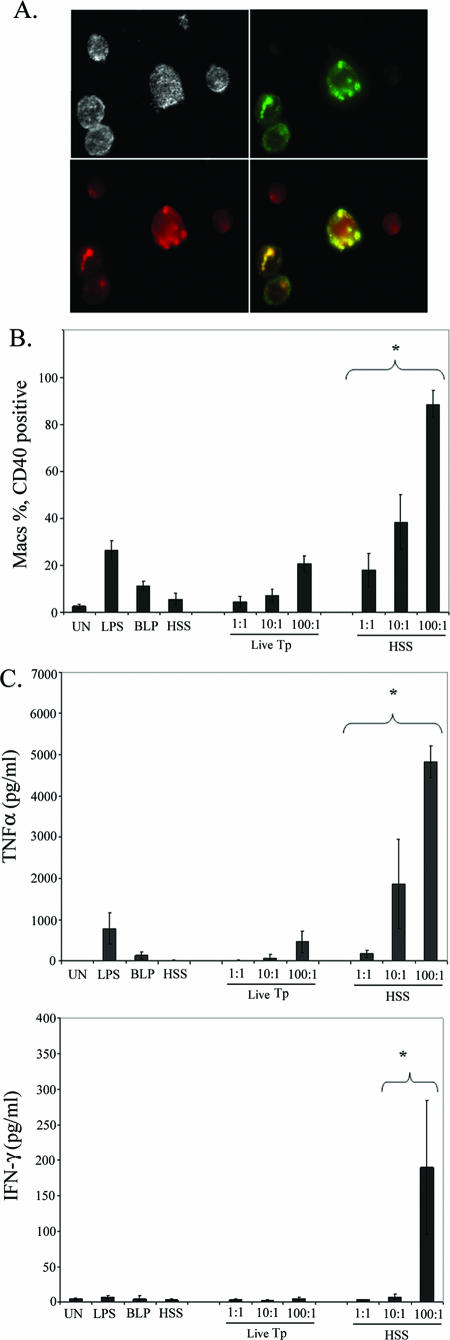
FIG. 6.
Enhanced inflammatory cytokine production following opsonophagocytosis of T. pallidum. A. Effect of HSS on the uptake of T. pallidum. PBMCs were incubated with live T. pallidum at a density of 10:1 for 4 h in the presence of 10% HSS and LysoTracker Red before IFA. The merged image (yellow) demonstrates colocalization of T. pallidum material (green) with lysosomal vacuoles (red). B and C. Internalization of T. pallidum (Tp) leads to enhanced macrophage activation (i.e., surface expression of CD40) (B) and greater production of TNF-α and IFN-γ (C). Monocytes were gated as the CD14+ population. Bar graphs represent the averages ± standard deviations from at least three experiments. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference between unopsonized and opsonized T. pallidum at equivalent MOIs. D. Intracellular cytokine staining for IFN-γ. Lymphocyte subpopulations within whole PBMCs were delineated via marker expression as described in Materials and Methods. Numbers in the dot plots represent the percentage of cells positive for IFN-γ; cytograms shown are representative of three experiments. TCR, T-cell receptor; PerCP, peridinin chlorophyll protein; UN, unstimulated.