FIG. 2.
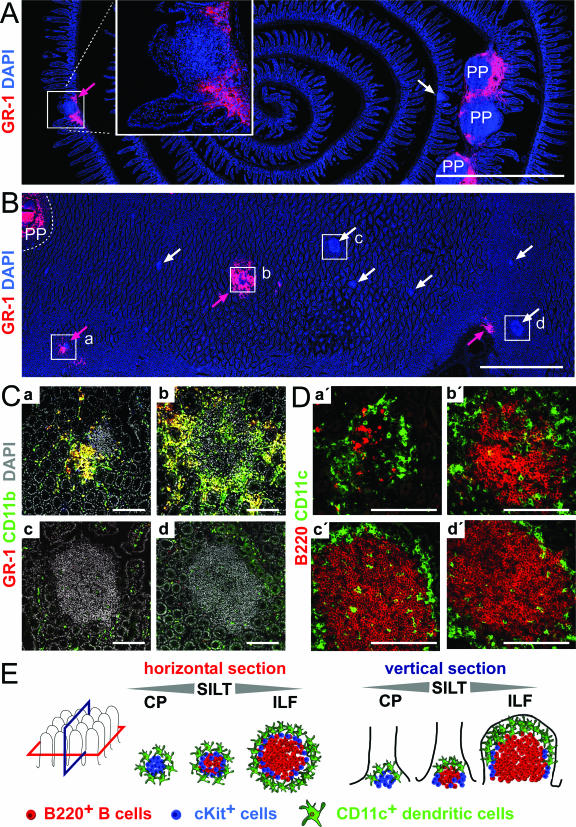
Inflammatory cell infiltrates localize to PP and SILT in the intestinal mucosa. At 7 days after Salmonella infection the localization of inflammatory cells in the intestinal mucosa was analyzed. (A) Vertical sections through small intestinal rolls were stained for nuclei (blue) and with anti-GR-1 antibody (red), which is indicative for inflammatory cells. Overview images that allow the assessment of large coherent areas of the section were automatically assembled. PP infiltrated by GR-1+ cells are designated PP, lymphoid aggregations devoid of GR-1-expressing infiltrating cells are indicated by white arrows, and lymphoid aggregation infiltrated by GR-1+ cells are indicated by red arrows. The boxed area is shown in a magnification in the inset image in panel A. (B) Horizontal sections through the intestinal wall were stained, analyzed, and annotated as described for panel A. Magnifications of the boxed regions illustrating two infiltrated lymphoid aggregations (a and b) and two structures that do not shown signs of inflammation (c and d) are shown in panel C. Nuclei are white, GR1+ cells are red, and CD11b+ cells are green. Double-positive cells expressing GR-1 and CD11b appear yellow. (D) On serial sections the area corresponding to the boxed regions was analyzed for CD11c+ dendritic cells (green) and B220+ B cells (red). (E) Schematic illustration of SILT as seen in vertical and horizontal sections. B220+ B cells, cKit+ cells, and CD11c+ dendritic cells constitute the major cellular components of such aggregates and localize in typical patterns. Small structures dominated by cKit+ cells are also designated CP. CP can develop into ILF in which a distinct B-cell follicle is predominant. However, the majority of all lymphoid structures display intermediate phenotypes that represent transitional phenotypes between CP and ILF. The entire spectrum of small lymphoid aggregation is referred to as SILT encompassing CP, ILF, and structures of intermediate phenotypes. Scale bars: 2 mm in panels A and B and 100 μm in panels C and D.