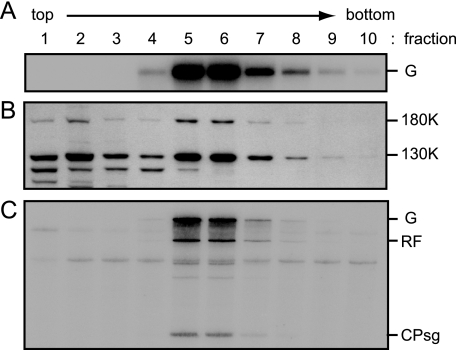
FIG. 3.
Fractionation of ToMV RNA-translated mdBYL by sedimentation in a sucrose gradient. A ToMV RNA (4 μg)-translated mdBYL reaction mixture (200 μl) was mixed with puromycin (0.2 mM in the resulting mixture) and incubated at 25°C for 10 min. This reaction mixture (200 μl) was loaded onto the 15 to 40% sucrose gradient and subjected to centrifugation. The gradient was manually fractionated into 10 fractions (220 μl per fraction; fractions 1 to 10, from top to bottom of the gradient). RNA and protein samples were prepared from these fractions and analyzed for panels A and B, respectively. In addition, each fraction was mixed with creatine phosphate (30 mM in the resulting mixtures from 1 M stock solution), creatine kinase (0.2 mg/ml in the resulting mixtures from a 10-mg/ml stock solution), ATP (0.75 mM in the resulting mixtures from 37.5 mM stock solution), and the P30BYL membrane suspension (1/20 volume of the resulting mixtures), and incubation was performed at 15°C for 1 h. After the incubation, 20 μl of each mixture was subjected to the RdRP reaction for panel C. (A) Presence of ToMV RNA. ToMV RNA was detected by Northern blot hybridization using a 32P-labeled P1M RNA probe (12). RNAs were denatured with glyoxal and separated in a 1% agarose gel. (B) Presence of ToMV replication proteins. The analysis was performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (C) ToMV RdRP activity. The RdRP reaction was performed in the presence of [α-32P]CTP. RdRP reaction products were analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. For abbreviations, see the legend to Fig. 1.