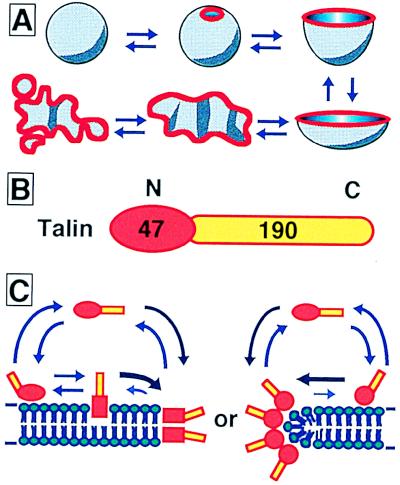
Figure 5.
Models showing the liposome transformation process, the domain structure of talin, and working models for protein association. (A) A closed spherical liposome transforms reversibly into an opened lipid bilayer membrane fragment, depending on the talin concentration. Red lines show talin localization, which is primarily along the free verge of the membrane. (B) Talin has a 47-kDa N-terminal membrane attachment domain and a 190-kDa C-terminal domain rich in α-helix. Actin and anti-talin monoclonal antibody interact with the C-terminal domain. The N- and C-terminal domains are colored red and yellow, respectively. (C) Talin penetrates into (Left) or associates with (Right) the membrane and is avoiding exposure of the hydrophobic portion at the edge of the lipid bilayer.