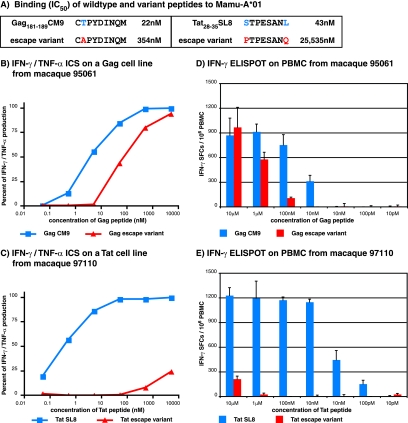
FIG. 2.
Recognition of wild-type and mutant epitopes in Gag and Tat as measured by IFN-γ/TNF-α ICS and IFN-γ ELISPOT assays. (A) Binding (50% inhibitory concentrations [IC50]) of the wild-type and variant peptides to Mamu-A*01 from a previous study (17). (B and C) IFN-γ/TNF-α ICS assay results for recognition of wild-type and escape variant peptides using Gag181-189CM9- (B) and Tat28-35SL8-specific (C) CD8+ T-cell lines derived from macaques 95061 and 97110, respectively. The data were normalized against the cytokine production when the highest wild-type peptide concentration was used. This value was considered the maximal cytokine response and was labeled as 100%. (D and E) Ex vivo IFN-γ ELISPOT assay results for recognition of wild-type and escape variant peptides using freshly isolated PBMC from macaque 95061 to test Gag reactivity (D) and from macaque 97110 to test Tat reactivity (E). Mean values from triplicate wells were calculated for each assay. The background, the mean of wells without peptide, was subtracted from each well. Mean responses of <50 SFC per 1 × 106 cells were not considered positive. The error bars in panels D and E indicate standard deviations for the triplicate wells.