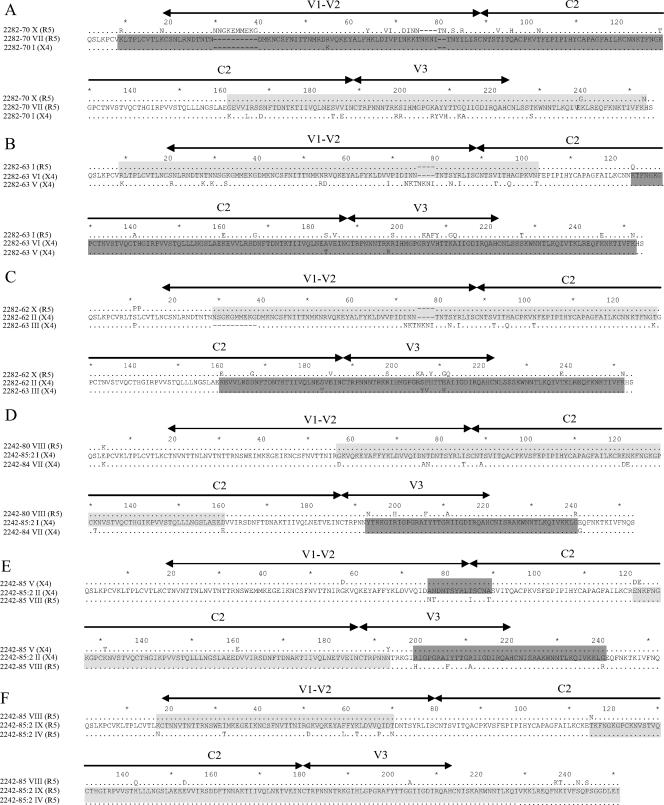
FIG. 3.
Amino acid sequences of recombinant clones. (A) R5 clone 2282-70 VII, (B) X4 clone 2282-63 VI, (C) X4 clone 2282-62 II X4, (D) X4 clone 2242-85:2 I, (E) X4 clone 2242-85:2 II, and (F) R5 clone 2242-85:2 IX. Recombinant sequences are shown in the middle of each alignment, and the parental sequences are shown above and below each recombinant sequence. Shaded regions indicate where the recombinants are most similar to one of the parental sequences. Regions shaded in light gray indicate similarity between the recombinant sequence and the R5 parental sequence, and regions highlighted in dark gray show regions of similarity between the recombinant and the X4 parent. The locations of the V1-V2, C2, and V3 regions are indicated. Dots represent identical amino acids between the recombinant and parental sequences. Recombinant clone 2242-85:2 II was most likely a result of a double-crossover event as indicated. The coreceptor usage is indicated in parentheses.