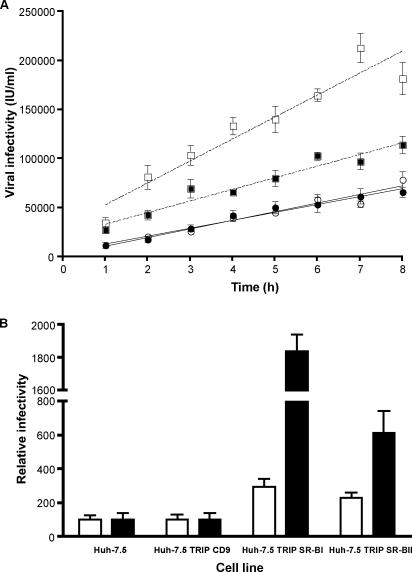
FIG. 3.
Overexpression of SR-BI and SR-BII in Huh-7.5 cells enhances HCVcc infection. (A) Parental (open circles) and transduced (filled circles) Huh-7.5 cells overexpressing human CD9, SR-BI (open squares), or SR-BII (filled squares) were incubated with J6/JFHcc for various times between 1 and 8 h; unbound virus was removed by washing, and the infection was allowed to proceed for 72 h. Both SR-BI- and SR-BII-transduced cells showed significantly elevated levels of infection (P < 0.05), with SR-BI cells showing a significantly higher rate of infection (22,360 infected cells/h/ml for SR-BI versus 8,800 to 11,000 for the other cell lines; P < 0.05; F test). Virus infectivity is expressed as the number of NS5A-positive cells or infected units (IU)/ml. (B) Parental and transduced cells were incubated with J6/JFHcc (white bars) or JFHcc (black bars) for 1 h, followed by a 72-h infection. Infected cells were visualized by staining them for intracellular NS5A, and virus infectivity for transduced cells was expressed relative to the parental cells. J6/JFH and JFH infectivities for parental Huh-7.5 cells were 11,000 ± 3,000 IU/ml and 2,400 ± 900 IU/ml, respectively. The error bars indicate the standard deviation above the mean of five individual infections.