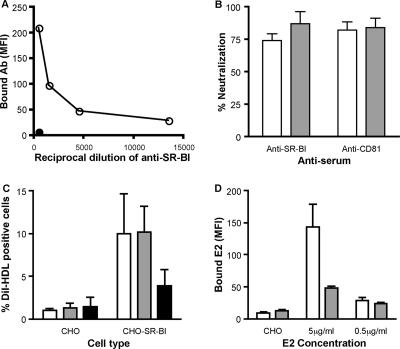
FIG. 6.
Anti-SR-BI serum inhibits cell culture- and plasma-derived J6/JFH infectivity. (A) Anti-SR-BI reactivity for Huh-7.5 cells (open circles). Control preimmune rabbit serum was tested at the highest dilution (filled circles). The data are expressed as the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (B) Huh-7.5 cells were incubated with anti-SR-BI and control preimmune sera at 1:500 or anti-CD81 MAb M38 and control isotype-matched Ig at 1 μg/ml for 1 h prior to infection with cell culture- (white bars) or plasma-derived (gray bars) J6/JFH. Infectivity was measured by quantifying NS5A-positive cells, and the percent neutralization of the receptor-specific antibodies was determined by comparing infectivity in the presence of the control antibodies. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean of three replicate infections. (C) CHO or CHO-SR-BI cells were preincubated with no antibody (white bars), control rabbit serum (gray bars), or anti-SR-BI (black bars) at 1/400 prior to incubation with DiI-labeled HDL (50 μg protein/ml) for 1 h at 4°C. The data are shown as the percentage of DiI-HDL-positive cells and represent the mean plus standard deviation of four independent experiments. (D) CHO-SR-BI cells were preincubated with control rabbit serum (white bars) or anti-SR-BI (gray bars) at 1/400 prior to incubation with sE2 at 5 and 0.5 μg/ml. Cell-bound E2 was detected with rat anti-E2 MAb 9/75 and Alexa 488 anti-rat Ig. Data are shown for sE2 (5 μg/ml) binding to control CHO cells and are expressed as the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) and standard deviation of duplicate experiments.