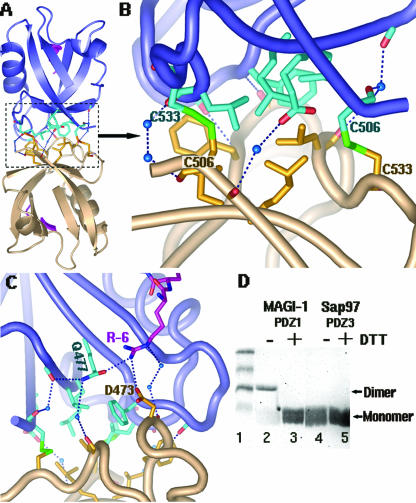
FIG. 5.
Dimer formation of MAGI-I PDZ1. (A) An overview of the MAGI-1 PDZ1 homodimer, shown in a ribbon diagram. Each monomer is shown in a different color (salmon or blue). The residues involved in contacts at the interface are shown as sticks. (B) A close-up view of the interactions at the dimer interface: two disulfide bridges are shown as green sticks, hydrogen bonds as dashed lines, and water molecules as blue spheres. Hydrophobic residues were found to cluster at the core of the interface. (C) Direct interaction of R-6 with D473 of the bottom monomer (salmon). This R-6 reaches across the dimer interface from the E6 peptide bound to the substrate groove of the top monomer (in blue). (D) Dimer formation of MAGI-1 PDZ1 in solution. About 10 μl of purified MAGI-1 PDZ1 (3.0 μg/μl) was treated with 10 μl SDS loading buffer in the absence or presence of 10 mM DTT (lanes 2 and 3), followed by a 12.5% SDS-PAGE analysis. Purified SAP97/Dlg PDZ3 was used as a control (lanes 4 and 5). The dimer form was detected only for MAGI-1 PDZ1 under nonreducing conditions (without DTT) (lane 2). All the PDZ domains run as a relatively diffused band as monomers, possibly due to their small size (∼8 kDa).