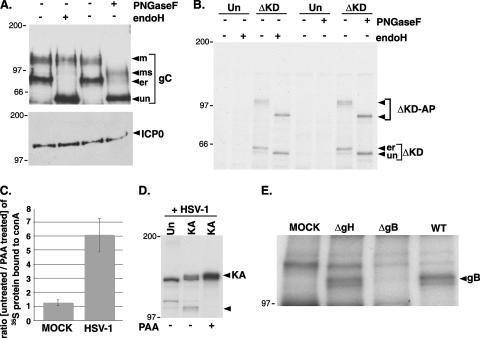
FIG. 5.
Identification of the 105-kDa PERK-associated protein as an HSV-1-encoded glycoprotein. (A) Specificity of endoglycosidases for viral glycoproteins. Detergent extracts from HSV-1-infected 293 cells were prepared at 10 hpi and either mock treated (−) or digested with endoglycosidase H (endoH) or PNGase F. At the conclusion of the digestion period, lysates were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using antisera specific for glycoprotein C or ICP0. The different glycosylated forms of gC are indicated to the right of the gel (un, unglycosylated; er, high-mannose form produced in the ER lumen; ms, mature post-Golgi form sensitive to PNGase F; m, fully mature glycosylated form). The migration positions of molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left of the gel. (B) 293 cells (untransfected [Un] or transfected with the ΔKD myc-tagged PERK expression plasmid) were infected with HSV-1 at high MOI. Following a 2-h incubation with 35S-labeled amino acids at 8 hpi, detergent lysates were prepared, immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc monoclonal antibody, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE as described in the legend to Fig. 4. Prior to electrophoresis, the immune complexes were incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of the indicated endoglycosidase. The migration positions of the immunoprecipitated proteins are indicated to the right of the gel (ΔKD-AP, 105-kDa protein associated with the myc-tagged ΔKD-PERK). The migration positions of molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) appear to the left of the gel. (C) Mock-infected or HSV-1-infected Vero cells either treated or untreated with PAA were radiolabeled with 35S-labeled amino acids for 15 min at 15 hpi. Detergent lysates were incubated with concanavalin A Sepharose, and after extensive washing, the bound proteins were eluted and quantified by counting in liquid scintillant. Results are expressed as the ratio of proteins synthesized in untreated cells compared to PAA-treated cells. (D) 293 cells (untransfected [Un] or transfected with the KA myc-tagged PERK expression plasmid [KA]) were infected with HSV-1 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of PAA. After radiolabeling with 35S-labeled amino acids for 2 h at 8 hpi, detergent lysates were prepared, immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody, and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 4. The migration positions of KA and the 105-kDa protein-associated protein are indicated by arrowheads to the right of the gel. The migration positions of molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) appear to the left of the gel. (E) 293 cells transfected with the KA myc-tagged PERK derivative were mock infected (MOCK) or infected with a gH-deficient mutant (ΔgH), a gB-deficient mutant (ΔgB), or wild-type virus (WT). Following a 2-h incubation with 35S-labeled amino acids at 8 hpi, detergent lysates were prepared, immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody, and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 3. The migration position of the 105-kDa glycoprotein B protein is indicated to the right of the gel.