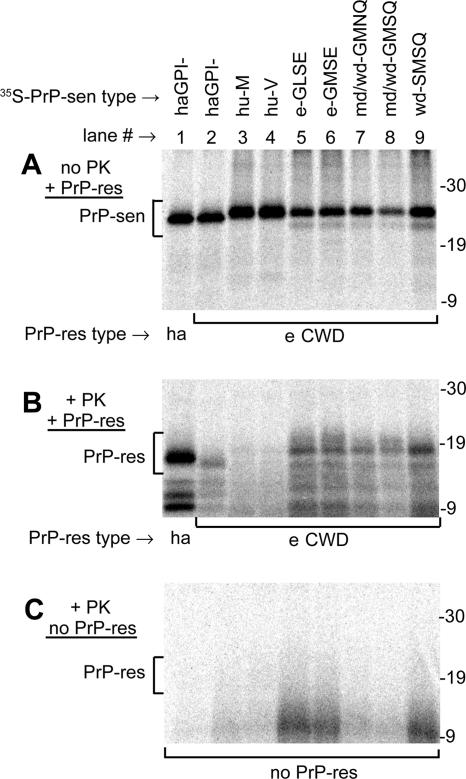
FIG. 1.
CFC reactions of various species' PrP-sen molecules induced by PrP-res. PrP-res isolated from either Sg hamsters (ha; lane 1 of each panel) or CWD-affected elk (e CWD; lanes 2 to 9) was incubated with various immunopurified 35S-PrP-sen molecules, identified at the tops of the lanes. (A) Aliquots (1/11) of each reaction mix that were not PK treated. The PrP-sen bands (bracketed; 22 to 26 kDa) were not glycosylated, as explained in Results. (B) Remaining portion of each reaction mix, treated with PK, resulting in the radiolabeled PrP-sen molecules being converted to PK-resistant PrP bands (PrP-res bracket; 16 to 18 kDa). (C) Parallel set of PK-digested reaction mixes incubated without PrP-res. The following PrP-sen molecules (descriptions are given in reference 20) were used in the conversion reactions: cervid PrP polymorphic types present in elk (e-GLSE and e-GMSE; lanes 5 and 6), PrP types present in mule deer and white-tailed deer (md/wd-GMNQ and md/wd-GMSQ; lanes 7 and 8) or white-tailed deer only (wd-SMSQ; lane 9), human Met/Met (hu-M; lane 3) and human Val/Val (hu-V; lane 4) PrP (amino acid residue 129 is given), and Sg hamster PrP lacking the GPI anchor (lanes 1 and 2; haGPI−). The md/wd GMNQ (lane 7) has recently been shown to be only the predicted translation product of an unexpressed pseudogene in deer (6). All data except those using hamster PrP molecules were previously published (20) and are shown here only to compare interspecies conversion efficiencies. The hamster conversion reactions were done at the same time as the other conversion reactions, using identical PrP-res isolates. The migration of molecular mass standards, in kilodaltons, is shown to the right of each panel.