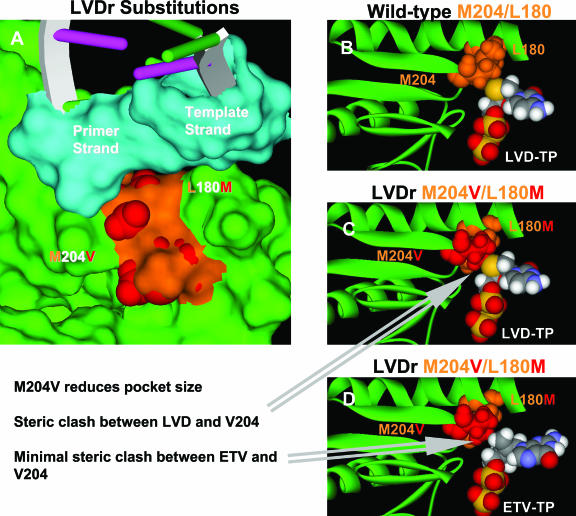
FIG. 6.
HBV RT with LVDr substitutions. (A) Surface of the HBV dNTP binding site (green), with the surfaces of the wild-type M204 and L180 residues shown in orange. The van der Waals surfaces of the LVDr substitutions M204V and L180M are shown in red. The surfaces of the HBV DNA active site bases are colored turquoise, and the extended DNA is depicted as a DNA ribbon. Note that the LVDr substitutions are in the pocket shown in Fig. 2. (B, C, and D) Ribbon representations highlighting the region around the dNTP binding site and showing the YMDD loop. The van der Waals surfaces of the wild-type M204 and L180 residues are colored orange, and the van der Waals surfaces of the LVDr substitutions M204V and L180M are shown in red. (B) Favorable close contact between LVD-TP and wild-type HBV (M204 and L180). (C) Steric hindrance between LVD-TP and LVDr M204V and L180M substitutions. (D) ETV-TP does not result in steric hindrance with the LVDr M204V and L180M substitutions.