Figure 2. Intergenic transcription represses Ubx in cis.
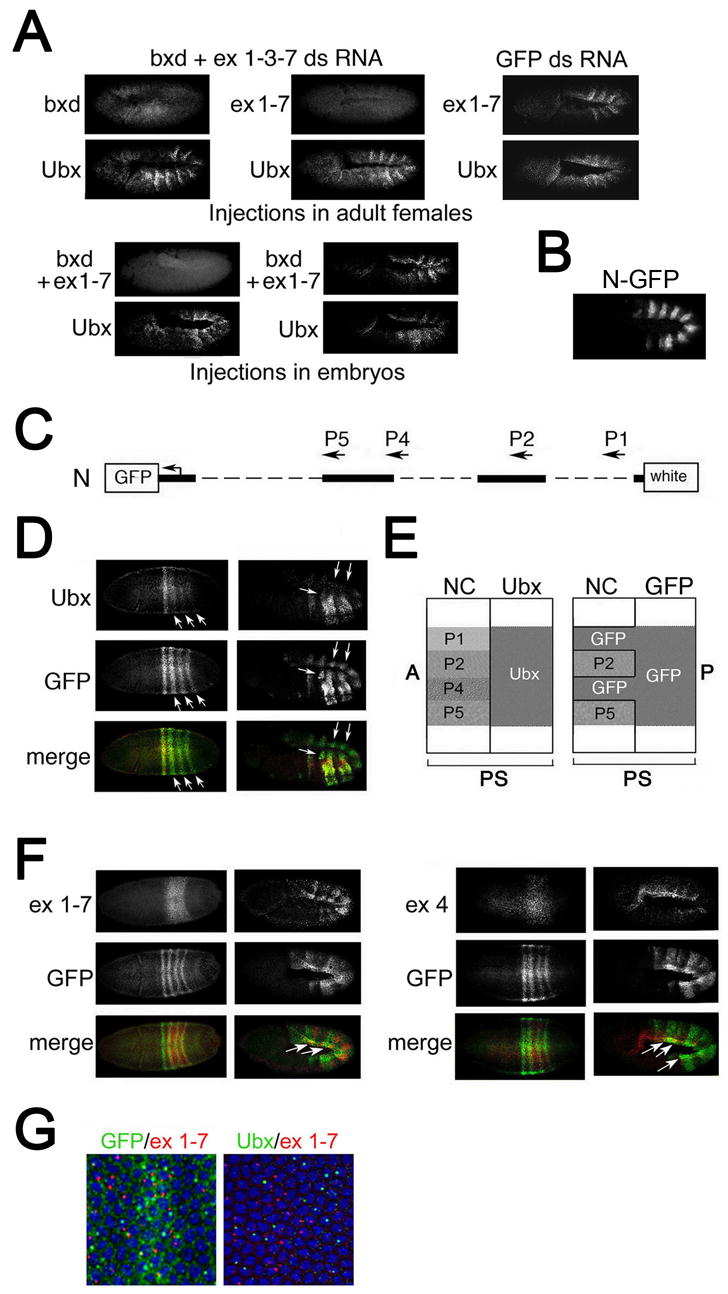
(A) Products of ncRNAs do not directly repress Ubx transcription. A mixture of dsRNAs specific to exons 1, 3, 7, and part of the bxd region, and control dsRNA specific to GFP were injected either into adult females (top panels) or into preblastoderm embryos. Embryos were analyzed by in situ hybridization with probes to Ubx, exons 1–7 and the mixture of probes to exons 1–7 and bxd, as indicated.
(B) Immunostaining of embryo carrying the Ubx-GFP transgenic construct N (see map in C) with GFP antibody.
(C) Map of the Ubx-GFP transgenic construct N. The transgene contains ncRNA promoters P2 and P5 but lacks promoters P1 and P4.
(D) The GFP reporter gene is ectopically expressed (arrows) at blastoderm and germband extension relative to endogenous Ubx.
(E) A diagram of predicted expression patterns of Ubx and GFP, assuming repression occurs only in cis. In the absence of the P1 and P4 promoters, the GFP transgene is expected to be expressed in cells where the corresponding endogenous RNAs are expressed. A, P, anterior and posterior of the embryo.
(F) Expression of the GFP reporter gene overlaps with expression of ncRNAs that are produced from the P1 (probe ex 1–7 left panels) and P4 (probe ex 4, right panels) promoters.
(G) Comparison of the expression of endogenous Ubx and the GFP reporter gene with RNA 1–7 at the blastoderm stage. Expression of GFP is seen in both cytoplasm and nuclei, and RNA 1–7 is detected in the nuclei of the same cells (left).
