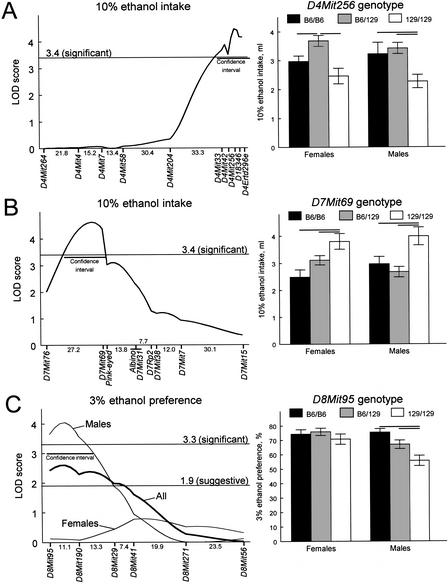
Figure 5.
Significant linkages. Left panels show results of interval mapping. Distances between markers in cM were estimated using MAPMAKER/EXP and are shown below the X-axis. Curves trace the logarithm of the odds ratio (LOD) scores calculated under locus-specific models using MAPMAKER/QTL. Horizontal lines show thresholds for suggestive and/or significant linkages under the locus-specific models (Lander and Kruglyak 1995). Confidence intervals (LOD drops of 1.0 from the peak) are shown by horizontal bars. Right panels show ethanol intakes or preferences by mice with different genotypes at a maker with the strongest linkage (means ± standard errors). Horizontal bars represent significant differences between groups (P<0.05, planned comparisons, two-way ANOVA). (A) A locus on distal chromosome 4 (Ap3q) affecting 10% ethanol intake. Left: B6-dominant model; the confidence interval spans region from 4 cM proximal to D4Mit33 to the telomeric end. Right: effects of D4Mit256 genotype, F(2,154) = 13.14, P = 0.000005, gender, F(1,154) = 0.11, P = 0.74, and their interaction, F(2,154) = 0.61, P = 0.55. (B) A locus on proximal chromosome 7 (Ap7q) affecting 10% ethanol intake. Left: B6-dominant model; the confidence interval spans region from 8 cM distally to D7Mit76 to 1 cM distally to D7Mit69. Right: effects of D7Mit69 genotype, F(2,160) = 11.08, P = 0.000031, gender, F(1,160) = 0.14, P = 0.71, and their interaction, F(2,160) = 2.19, P = 0.12. (C) A male-specific locus on proximal chromosome 8 (Ap8q) affecting 3% ethanol preference. Left: additive model; the confidence interval spans region from the centromeric end to 6 cM distally to D8Mit190. Right: effects of D8Mit95 genotype, F(2,161) = 6.40, P = 0.0021, gender, F(1,161) = 8.69, P = 0.0037, and their interaction, F(2,161) = 2.90, P = 0.058.