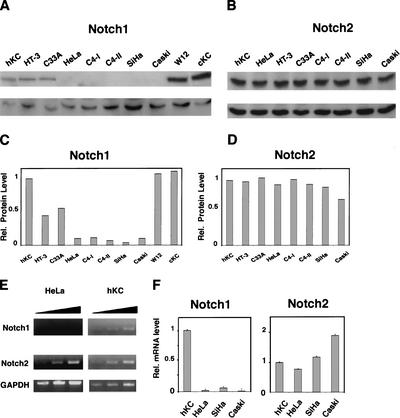
Figure 1.
Specific down-modulation of endogenous Notch1 expression in cervical carcinoma cells. (A,B) Total cell extracts from primary human foreskin keratinocytes (hKC), a panel of cervical carcinoma cell lines, cervical keratinocytes (cKC), and a keratinocyte cell line with episomal HPV (W12) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against Notch1 (C-20) and Notch2 (C65) as indicated (upper panels). Immunoblotting with antibodies against Cdk2 was used as an equal loading control (lower panels). Similar results were obtained in at least two other experiments, including use of Tan-20 antibodies for detection of Notch1, and of anti-β actin antibodies for an equal loading control. (C,D) Densitometric scanning of the autoradiographs shown in A and B was used for quantification of the relative levels of Notch1 and Notch2 proteins in human primary keratinocytes versus the other cells. Cdk2 expression was used for internal value normalization. (E) Total RNA from human primary keratinocytes and HeLa cells was analyzed by RT-PCR with oligonucleotide primers specific for the 3′-untranslated regions of the Notch1 and Notch2 transcript and for GAPDH as indicated. Each sample was analyzed in three serial dilutions (1:1, 1:10, 1:100). (F) Total RNA from human primary keratinocytes and various carcinoma cells was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR with primers specific for the 3′-untranslated regions of the Notch1 and Notch2 transcripts as indicated.Values were normalized for β-actin expression and expressed as relative levels in reference to primary human keratinocytes. All RNAs were tested in triplicate samples, and the standard deviation is indicated.