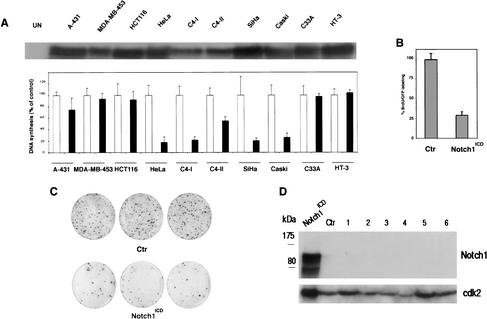
Figure 5.
Specific growth inhibitory effects of activated Notch1 in cervical carcinoma cell lines. (A) Epidermoid carcinoma (A-431), breast (MDA-MB-453), colon (HCT116), and indicated cervical carcinoma cells were infected with a recombinant adenovirus expressing activated Notch1 (Ad-Notch1) or green fluorescence protein (Ad-GFP). (Upper panel) Total cell extracts from the indicated cell lines infected with the Ad-Notch1 virus were examined for levels of activated Notch1 expression by immunoblotting with the corresponding antibody. (Lower panel) Cellular DNA synthesis was determined by 3H-thymidine incorporation assay 36 h after infection. Cells were tested in triplicated wells, and the standard deviation is indicated. The slight differences in sensitivity of the various HPV-positive carcinoma cell lines to Ad-Notch1 growth inhibition are likely owing to the different growth patterns of these various cells. In fact, some of these cell lines tend to grow in tightly packed clusters, with cells at the center of these clusters being less susceptible to adenoviral infection (as evaluated by expression of the GFP marker, which is also transduced by the Ad-Notch1 virus). (B) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid expression vector for activated Notch1 (Notch1ICD) or empty vector control (Ctr) together with trace amounts of a GFP expression vector for identification of transfected cells. Cells were labeled with BrdU for 3 h prior to termination of the experiment (36 h after transfection). The BrdU-labeling index of GFP-positive transfected cells was determined by counting in each case a minimum of 120 cells from six independent fields. Values are expressed as percentages relative to the control. Similar results were obtained in two other independent experiments. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid expression vector for activated Notch1 (Notch1ICD) or empty vector control (Ctr) together with trace amounts of an expression vector for G418 resistance. The same number of transfected cells was plated and cultured in triplicate dishes in the presence of antibiotic selection for 2 wk. The number of macroscopically visible colonies formed by cells transfected with the control versus activated Notch1 expression vector was 311 (±20) and 68 (±8), respectively. Similar differences were observed in two other independent experiments. (D) HeLa cells at 24 h after transfection with the activated Notch1 vector (Notch1ICD), and cells from six independent colonies (1–6) that emerged from cultures transfected with the same vector after 2 wk of G418 selection (as in C), were analyzed for levels of Notch1 expression by immunoblotting with the corresponding specific antibodies. (Ctr) Cells from a colony of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector control. The immunoblot was reprobed with anti-cdk2 antibody for an equal loading control.