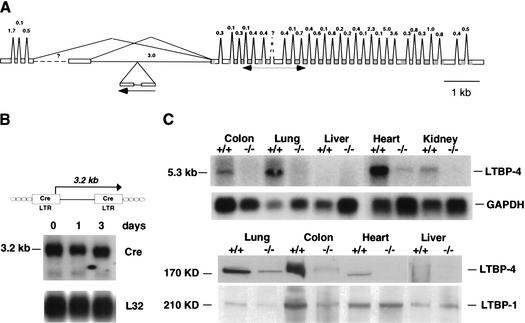
Figure 3.
Gene trap disruption of the LTBP-4 gene locus. (A) Predicted intron/exon structure of the mouse LTBP-4 gene with the gene trap integration site. The exon/intron structure was compiled by using the mouse cDNA sequences for the short and long 5′ splice variants (GenBank accession nos. AF410798 and AF410799), the human cDNA sequences for the various 5′ splice variants (GenBank accession nos. NM_003573, AF054502, AF054501, AF051345, AF051344, and Y13622), and the available genomic sequence of mouse chromosome 7 (GenBank accession no. AC073713). EGF domains and 8Cy repeats are shaded in dark and light gray, respectively. (B) Structure of the U3Cre gene trap provirus (top) and Northern blot analysis of 3C7 ES cells (bottom). Polyadenylated RNAs from ES cells that were grown for 3 d in the absence of LIF and feeder layers were blotted onto nylon filters and hybridized to 32P-labeled Cre- or ribosomal protein L32-specific probes. (C) LTBP-4 expression in wild-type (+/+) and homozygous 3C7 (−/−, hypomorphic LTBP-4 alleles) mice. (Top) Northern blot analysis. Polyadenylated RNAs from selected mouse tissues were blotted onto nylon filters and hybridized to a 32P-labeled LTBP-4 probe. The probe was a 505-nt fragment extending between nucleotides 882 and 1367 of the LTBP-4S cDNA (GenBank accession no. AF410798; for location, see A). This sequence stretch is shared by all known splice variants. (Bottom) Immunoblotting with human anti-LTBP-4 and anti-LTBP-1 antibodies. Proteins from selected tissue digests (see Materials and Methods) were separated on denaturing polyacrylamide gels under reducing conditions, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and reacted with polyclonal anti-LTBP-1 or anti-LTBP-4 antibodies raised against the third and fourth 8-Cystein repeats that are shared between known splice variants (Saharinen et al. 1998).