Figure 1.
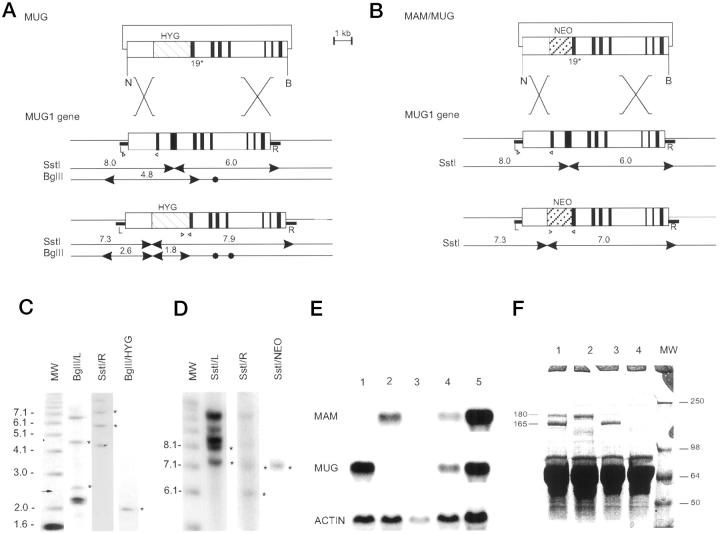
Generation of mice deficient in MUG and in both MAM and MUG. A: Recombinant DNA construct (top) based on the MUG1 gene (middle) and predicted structure of the targeted MUG1 gene (bottom). The positive selection marker is represented by a hatched box marked HYG. NheI (N) and BamHI (B) restriction sites are marked by arrowheads for diagnostic fragments and closed circles for irrelevant sites. R and L represent genomic DNA probes. B: Recombinant DNA construct (top) to target the MUG1 gene in ES cells with a targeted MAM gene. 34 Structure of the MUG1 gene (middle) and recombinant MUG1 gene (bottom) with positive selection marker represented by a hatched box marked NEO. Diagnostic SstI restriction fragments are indicated. C and D: Southern blots of ES cell lines with recombined MUG1 and MAM/MUG1 genes, respectively, digested with SstI or BglII and hybridized with DNA probes, ie, R, L, HYG, or Neo, as indicated. Standards on the right are in kilobasepairs and asterisks denote diagnostic bands described in the text. E: Northern blot of liver RNA from mice with genetic status MAM−/− (Lane 1), MUG1−/− (Lane 2), MAM−/−MUG1−/− (Lane 3), MAM+/−MUG1+/− (Lane 4), and wild-type (Lane 5). Blot was sequentially hybridized with cDNA probes specific for MAM, MUG1, and actin. F: SDS-PAGE of plasma from wild-type mouse (Lane 1), MAM−/− mouse (Lane 2), MUG1−/− mouse (Lane 3), and MAM−/−MUG−/− mouse (Lane 4). Indicated are the 165-kd MAM subunit and the 180-kd MUG1 subunit with apparent MW of markers (Lane MW) shown in kilodaltons.