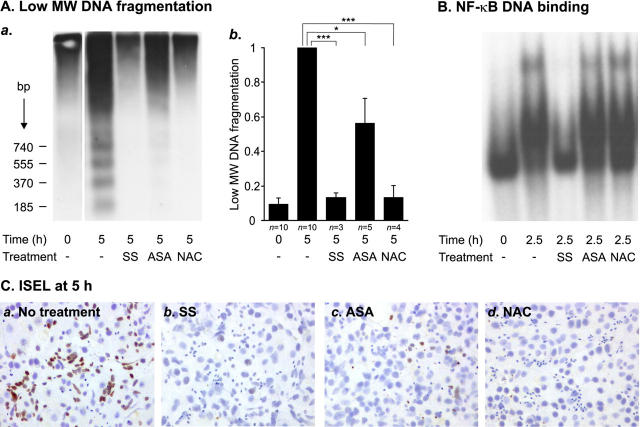
Figure 5.
Effects of NF-κB inhibitors on human testicular apoptosis and NF-κB activation. Segments of human seminiferous tubules were cultured in serum-free conditions in the absence or presence of 5 mmol/L SS, 5 mmol/L ASA, or 100 mmol/L NAC. After culture for 2.5 hours, samples of the tubules were snap-frozen and nuclear protein extracts were prepared for analysis of NF-κB activity. The rest of the tubules were cultured for 5 hours and analyzed for apoptotic DNA fragmentation by Southern blot and ISEL analyses. A: Southern blot analysis of apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Equal amount (1 μg) of the total DNA from each sample was 3′-end labeled with Dig-dd-UTP, after which the DNA samples were electrophoresed and blotted onto nylon membranes and the labeled apoptotic DNA fragments were detected with chemiluminescence as described in Materials and Methods. a: Radiograph from a representative experiment in which 5 mmol/L SS, 5 mmol/L ASA, or 100 mmol/L NAC was added to the culture medium. b: Quantification of SS-, ASA-, and NAC-mediated inhibition of low molecular weight DNA (<1.3 kb) fragmentation. Each value represents a mean of the indicated number of independent experiments ± SEM. In all experiments, SS and NAC blocked apoptosis extremely effectively. The anti-apoptotic effect of ASA was strong in three experiments but only moderate in two experiments, which led to the variation indicated in the figure. *, P < 0.05; ***, P = 0.001. B: EMSA showing the effects of 5 mmol/L SS, 5 mmol/L ASA, or 100 mmol/L NAC on testicular NF-κB DNA-binding activity. Nuclear protein extracts (10 μg) were analyzed for NF-κB DNA-binding activity, as described in the legends to Figures 1 and 2 ▶ ▶ and in Materials and Methods. The result is representative of three independent experiments. C: ISEL analysis of the inhibition of germ cell apoptosis by SS, ASA, or NAC. Apoptotic DNA fragments in squash preparations of seminiferous tubules cultured for 5 hours in serum-free conditions in the absence or presence of indicated compounds were detected by 3′-end labeling with Dig-dd-UTP as described in Materials and Methods. a: A great number of ISEL-positive germ cells were observed in the seminiferous tubules after 5 hours of exposure to apoptosis-inducing conditions. Germ cell death was effectively suppressed by 5 mmol/L SS (b), 5 mmol/L ASA (c), or 100 mmol/L NAC (d). The overall morphology of the testicular cells was not disturbed by the treatments.