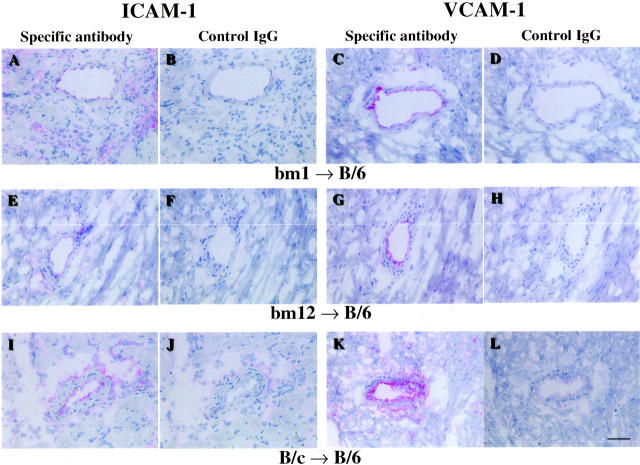
Figure 5.
Immunohistochemical staining for adhesion molecules. Representative sections from bm1, bm12, or B/c to B/6 allografts 7 days after transplant, without 4-hour cold storage. Scale bar, 50 μm. A: ICAM-1 staining of a section from a bm1 to B/6 allograft. ICAM-1 expression is increased on the endothelium and on graft infiltrating mononuclear leukocytes. B: Negative control staining for A using isotype-matched hamster IgG. C: VCAM-1 staining of a section from a bm1 to B/6 allograft. VCAM-1 expression is increased on the endothelium and on some of graft-infiltrating mononuclear leukocytes. D: Negative control staining for C using isotype-matched rat IgG. E: ICAM-1 staining of a section from a bm12 to B/6 allograft. F: Negative control staining for E. G: VCAM-1 staining of a section from a bm12 to B/6 allograft. H: Negative control staining for G. I: ICAM-1 staining of a section from a B/c to B/6 allograft. J: Negative control staining for I. K: VCAM-1 staining of a section from a B/c to B/6 allograft. L: Negative control staining for K. Strong expression of both ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 was observed at day 7 for all allografts. Four-hour cold ischemia did not have any significant effect on the expression of these cell adhesion molecules at day 7 post-transplant. Expression of both ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 was most pronounced in B/c to B/6 allografts, reflecting the most severe acute rejection.