Figure 6.
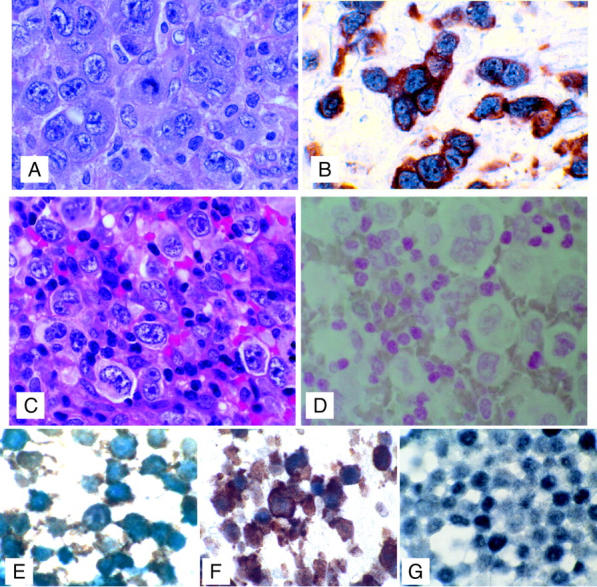
Co-expression of ALK and c-Myc in tumor cells. Top: A: H&E-stained section of CD30-positive, ALK-positive, T-cell ALCL. B: Dual immunohistochemical staining demonstrating co-expression of c-Myc (blue, alkaline phosphatase detection, nuclear stain) with ALK (t2;5) translocation protein product (detected with brown diaminobenzidine, cytoplasmic stain) in tumor cells. Representative of 15 ALK-positive cases. Middle: C: H&E-stained section of CD30-positive, ALK-negative, T-cell ALCL. D: Dual immunohistochemical staining (with nuclear red counterstain) demonstrating lack of c-Myc (blue alkaline phosphatase detection, nuclear stain) and ALK (t2;5 translocation protein product detected with brown diaminobenzidine, cytoplasmic stain) in tumor cells. Representative of six ALK-negative cases (three T-large cell lymphomas and three T-cell lymphoblastic lymphomas). Bottom: Double-label immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed cell lines with ALK-1 (diaminobenzidine detection, brown) and c-Myc (alkaline phosphatase blue, blue-black color) showing co-expression of ALK-1 and c-Myc in the ALK-positive ALCL cell lines SUDHL-1 (E) and Karpas 299 (F) but expression of c-Myc only in the non-ALK-expressing T-cell lymphoma cell line MAC2A (G). Original magnifications: ×100 (A–D); ×1000 (E–G).
