Figure 6.
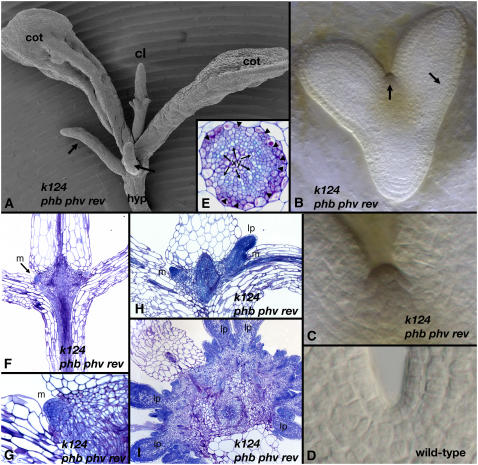
The Phenotype of kan1 kan2 kan4 phb phv rev.
(A) A 14-d-old kan1 kan2 kan4 phb phv rev seedling (k124 phb phv rev) has two cotyledons (cot) and ectopic leaf-like outgrowths developing from the hypocotyl (arrows), similar to kan1 kan2 kan4 seedlings (cf. with Figure 4A, same age). In addition, in kan1 kan2 kan4 phb phv rev seedlings, a single radial central leaf (cl) develops in the position normally occupied by the SAM. The central leaf exhibits outgrowths on its distal end and is radialized toward its proximal end.
(B) to (D) The central leaf substituting for the SAM in kan1 kan2 kan4 phb phv rev is initiated during embryogenesis, with subepidermal periclinal cell divisions giving rise to a leaf primordium (C) instead of anticlinal cell divisions, as in wild-type SAMs (D). Arrows in (B) indicate areas of periclinal cell divisions.
(E) The vascular bundle at the proximal end of the central leaf is radialized with patches of phloem (arrows) surrounding a ring of xylem (xy) and parenchyma cells located at the center.
(F) to (I) Ectopic meristems (m) develop around the base of the central leaf, as seen in longitudinal sections through the central leaf ([F] to [H]; [G] is a closeup of [F]), and give rise to leaf primordia (lp) (I).