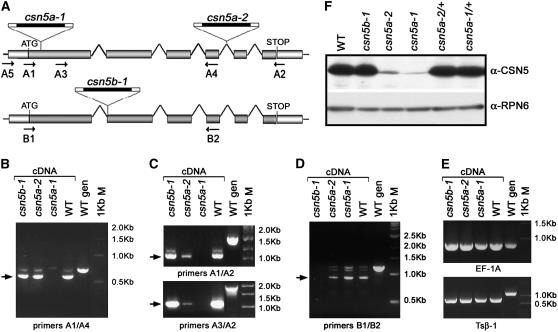
Figure 1.
Expression Analyses of csn5 Single Mutants.
(A) Structures of the Arabidopsis CSN5A (At1g22920) and CSN5B (At1g71230) loci and graphical representation of the T-DNA insertion mutants used in this study. Arrows indicate the positions and orientations of the gene-specific primers used for the RT-PCR analyses.
(B) to (E) RT-PCR analyses of the wild type and csn5b-1, csn5a-2, and csn5a-1 homozygous mutants. Different sets of gene-specific primers were used to selectively amplify the CSN5A 5′ (B) and full-length (C) transcripts or the CSN5B transcript (D). The eEF-1A (E) (top panel) and Tsβ1 (E) (bottom panel) transcripts were used as positive controls for the RT-PCR analyses. Genomic DNA was used as a positive control for the PCR. Arrows indicate the PCR products corresponding to mature CSN5A and CSN5B transcripts. The csn5a-2 mutants still express low levels of full-length CSN5A mRNA.
(F) Detection of CSN5 proteins from the wild type and null homozygous csn5b-1 and weak (csn5a-2) or null (csn5a-1) homozygous and heterozygous csn5a mutants with anti (α)-CSN5 polyclonal antibodies, which recognize both CSN5A and CSN5B isoforms. Equal protein loading was confirmed using α-RPN6 antibody. The csn5a-2 mutants express low levels of CSN5A protein in addition to traces of CSN5B.