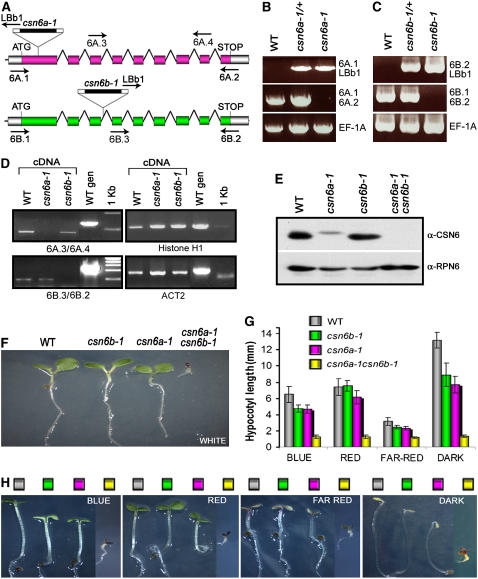
Figure 4.
The MPN Subunits CSN6A and CSN6B of CSN Are Essential and Functionally Redundant.
(A) Structures of Arabidopsis CSN6A (At5g56280) and CSN6B (At4g26430) loci and graphical representation of the corresponding T-DNA insertion lines used in this study. Arrows represent the positions and orientations of the gene-specific primers and the left border T-DNA primer (LBb1) used for the PCR-based genotype (6A.1, 6A.2, 6B.1, and 6B.2) and RT-PCR (6A.3, 6A.4, 6B.2, and 6B.3) analyses.
(B) and (C) PCR-based genotype analyses of Arabidopsis wild type and csn6a-1 (B) or wild type and csn6b-1 (C) heterozygous and homozygous mutants. The genomic sequence of the EF-1A locus was used as a positive control for the PCR.
(D) RT-PCR analyses of the wild type and csn6a-1 and csn6b-1 mutants. Primers 6A.3/6A.4 and 6B.2/6B.3 were used to selectively amplify the CSN6A (top left panel) or CSN6B (bottom left panel) mature transcripts, as indicated. Sets of primers specific for histone H1 (top right panel) and ACT2 (bottom right panel) were used as positive controls for cDNA calibration.
(E) Detection of CSN6 proteins from the wild type and single and double null homozygous mutants by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analyses with anti (α)-CSN6 polyclonal antibodies, which recognize both CSN6A and CSN6B subunits. Equal protein loading was confirmed using α-RPN6 antibody.
(F) Phenotypes of 5-d-old wild-type, csn6b-1, csn6a-1, and csn6a-1 csn6b-1 seedlings grown in continuous white light.
(G) and (H) Hypocotyl elongation (G) and phenotypes (H) of wild-type and csn6 mutant seedlings grown for 5 d in darkness or different light qualities, as indicated (see Methods). Values shown in (G) represent means of 25 seedlings ± sd. The colored boxes shown in (H) correspond to the genotypes indicated in (G).