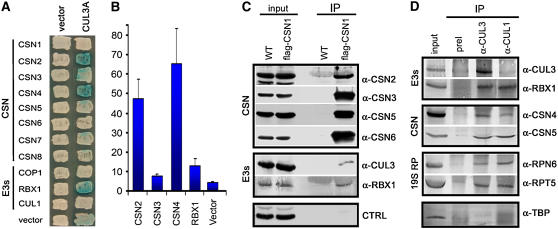
Figure 8.
The in Vivo Association of CSN, CUL3-Based E3 Ligases, and the 26 Proteasome.
(A) In vitro interaction between Arabidopsis CUL3A, RBX1, and CSN subunits by yeast two-hybrid assay. Blue colonies indicate LacZ production and thus protein interaction.
(B) Colonies that tested positive for interactions in (A) were subjected to liquid quantitative assays to verify the strength of the binding. Numbers shown on the y axis are means of two experiments. For each experiment, the numbers on the y axis were calculated as mean values of at least six independent transformants. Error bars represent sd.
(C) CSN specifically associates with the CUL3A-RBX1 E3 module in vivo. Total soluble protein extracts (input) from wild-type and FLAG-CSN1 transgenic seedlings were incubated with monoclonal anti-FLAG–conjugated agarose (α-FLAG; see Methods), and the immunoprecipitates (IP) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against CSN2, CSN3, CSN5, CSN6, CUL3, and RBX1. The control represents a protein band recognized by α-CSN2 antibody.
(D) CUL3 specifically associates with CSN and the proteasome in vivo. Total soluble protein extracts (input) from wild-type seedlings were incubated with CUL3 preimmune serum (preI) or with CUL3 and CUL1 antibodies coupled to protein A-agarose (see Methods), as indicated. The immunoprecipitates (IP) were then separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against CUL3, RBX1, CSN4, CSN5, RPT5, RPN6, and TBP.