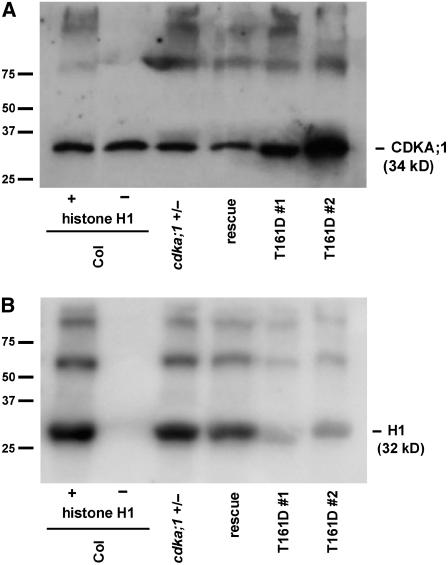
Figure 4.
In Vitro Histone H1 Kinase Assays of T161D Plants.
(A) Of a crude plant extract derived from flower buds, 150 μg of total protein was subjected to a p13Suc1 pull-down and a subsequent kinase assay, separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with a CDK antibody (α-PSTAIRE) to ensure equal loading of the beads. As controls, Columbia (Col), heterozygous cdka;1 mutants, and homozygous mutant plants carrying the rescue construct ProCDKA;1:CDKA;1 were used.
(B) Two independent homozygous mutant lines rescued by ProCDKA;1:CDKA;1T161D (lines #1 and #2) were investigated for their in vitro kinase activity toward their substrate histone H1. The homozygous mutant T161D lines show a strong decline in kinase activity.
Similar results were observed in at least three independent repetitions; the left two lanes show loading (A) and phosphorylation (B) in control reactions of CDK pull-downs from wild-type material with (+) and without (−) histone H1.