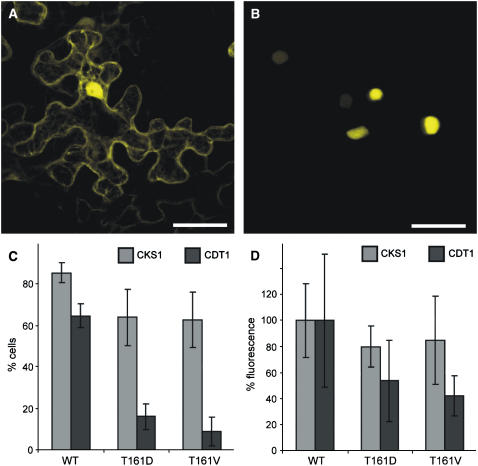
Figure 5.
Enzyme–Substrate Interaction of CDKA;1 Variants.
(A) CDKA;1 interacts with the nonsubstrate CKS1 in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The same pattern was observed for CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V. Bar = 40 μm.
(B) CDKA;1 binds to the bona fide substrate CDT1 predominantly in the nucleus. Although much weaker, CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V interaction with CDT1 also was observed. Bar = 40 μm.
(C) and (D) Quantification of the interaction between different CDKA;1 variants and CKS and CDT1. Quantifications were done with at least 25 cells each, and error bars represent sd from at least three independent experiments.
(C) The number of fluorescent cells in a given area of 25 cells is reduced slightly in interactions of the nonsubstrate CKS1 with the T-loop mutants CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V compared with wild-type CDKA;1. By contrast, the number of YFP-positive cells is strongly reduced in interactions of the substrate CDT1 with the T-loop mutants CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V compared with wild-type CDKA;1. The number of positive cells is most reduced in interaction assays with CDKA;1T161V.
(D) Fluorescence intensities are reduced slightly in interactions of the nonsubstrate CKS1 with the T-loop mutants CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V compared with wild-type CDKA;1, which was arbitrarily set to 100%. By contrast, the YFP intensities are strongly reduced in interactions of the substrate CDT1 with the T-loop mutants CDKA;1T161D and CDKA;1T161V compared with wild-type CDKA;1; the fluorescence reduction is most pronounced in interaction assays with CDKA;1T161V.