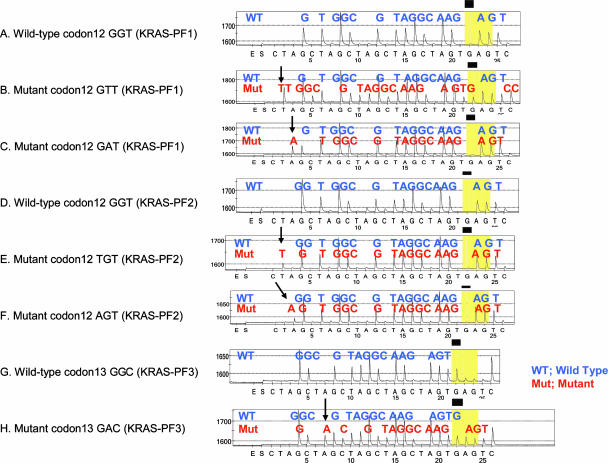
Figure 2.
Pyrograms of wild-type and mutant KRAS. A: Wild-type codon 12 by the KRAS-PF1 primer. B: c.35G>T (codon 12 GTT) mutation by the KRAS-PF1 primer. C: c.35G>A (codon 12 GAT) mutation by the KRAS-PF1 primer. D: Wild-type codon 12 by the KRAS-PF2 primer. E: c.34G>T (codon 12 TGT) mutation by the KRAS-PF2 primer. F: c.34G>A (codon 12 AGT) mutation by the KRAS-PF2 primer. G: Wild-type codon 13 by the KRAS-PF3 primer. H: c.38G>A (codon 13 GAC) mutation by the KRAS-PF3 primer. Arrows indicate the presence of mutant alleles. Note that B, C, E, F, and H show the presence of wild-type sequence, which is derived from non-neoplastic cells in tumor (and a normal allele in tumor cells).