Abstract
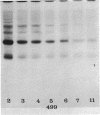
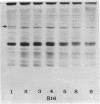
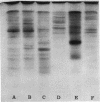
The flat gel acrylamide electrophoresis technique was standardized and applied to the comparison of four species of porcine mycoplasmas. Clear differences were observed between these species, and differences were seen among the strains of Mycoplasma hyosynoviae. The clarity of the patterns and the number of bands developed was influenced by the amount of protein in the extract and the age of the culture. The technique allows the comparison of several protein extracts in parallel without the problems associated with the rearrangement of separate gel columns.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akroyd P. Acrylamide gel slab electrophoresis in a simple glass cell for improved resolution and comparison of serum proteins. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jun;19(3):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Yu B. Characterization of canine mycoplasmas by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunodiffusion. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.295-299.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DelGiudice R. A., Carski T. R., Barile M. F., Lemcke R. M., Tully J. G. Proposal for classifying human strain navel and related simian mycoplasmas as Mycoplasma primatum sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):439–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.439-445.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger J. D., Jasper D. E. Polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins of mycoplasma isolated from cattle and horses. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Apr;33(4):769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw K. A. Electrophoretic patterns of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):493–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis N. F. A new porcine mycoplasma species: mycoplasma suidaniae. Acta Vet Scand. 1970;11(3):487–490. doi: 10.1186/BF03547974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gois M., Pospisil Z., Cerny M., Mrva V. Production of pneumonia after intransal inoculation of gnotobiotic piglets with three strains of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Jul;81(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Antigenic differences within the species Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):469–477. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Ecuyer C. Enzootic pneumonia in pigs: propagation of a causative mycoplasma in cell cultures and in artificial medium. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Jan;33(1):10–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasma taxonomy studiedy electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.687-694.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Identification of Mycoplasma and other microorganisms by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1807-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. H. A previously unreported serotype of porcine mycoplasma. Vet Rec. 1970 Aug 15;87(7):214–215. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.7.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S. Analysis of the electrophoretic pattern of mycoplasma proteins for the identification of canine mycoplasma strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. F., Karmon J. A. Heterogeneity among strains of Mycoplasma granularum and identification of Mycoplasma hyosynoviae, sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):707–713. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.707-713.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., MacLennan D. H., Tzagoloff A., Stoner C. D. Studies on the electron transfer system. LXVII. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the mitochondrial electron transfer complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., Baxendale W., Sayer L. J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of lysates of mycoplasmas. Res Vet Sci. 1970 Jul;11(4):397–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]