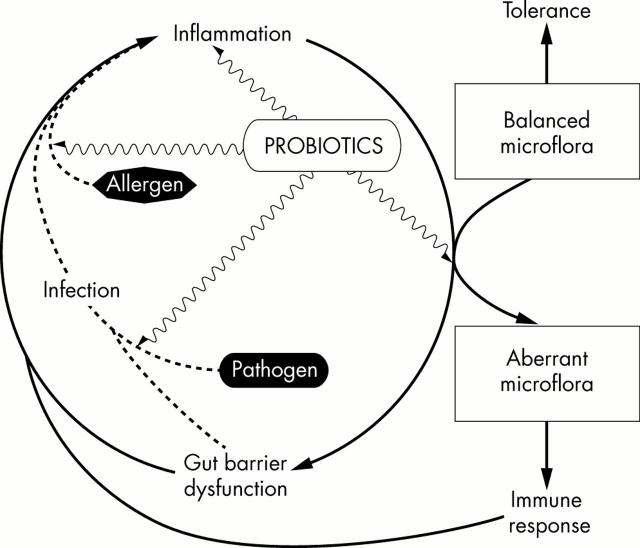
Figure 2 .
Gut microflora in inflammation. Inflammation may direct the composition and function of a balanced normal microflora to become aberrant and immunogenic, leading to perpetuation of the inflammation and gut barrier dysfunction. Probiotic bacteria may counteract the inflammatory process by enhancing the degradation of enteral antigens, reducing the secretion of inflammatory mediators, and promoting the normalisation of indigenous flora and the exclusion of pathogens.