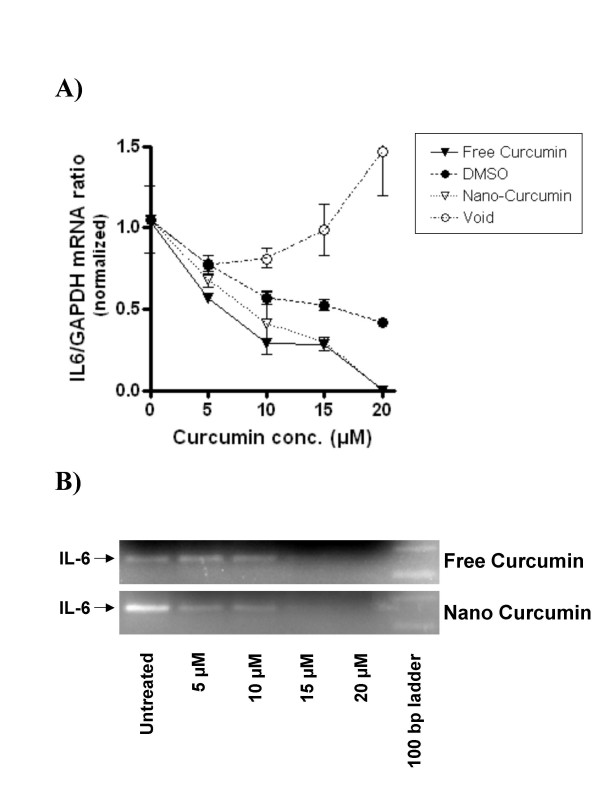
Figure 13.
Nanocurcumin inhibits IL-6 synthesis in a dose-dependent manner. PBMCs of a healthy donor were incubated with PHA to stimulate T-cells, and LPS to trigger monocyte-derived cytokine production. Cells were exposed to increasing concentrations (0, 5, 10, 15 or 20 μM) of free or nanocurcumin, or equivalents amounts of DMSO or void nanoparticles, respectively for 24 h. Quantitative RT-PCR revealed dose-dependent inhibition of IL-6 mRNA synthesis by both curcumin formulations (A). Complete blockade of IL-6 transcripts was achieved by adding free or nanocurcumin at 20 μM, even in PBMC co-stimulated with PHA and LPS (B). The error bars represent mean and standard deviations of experiments performed in triplicate.