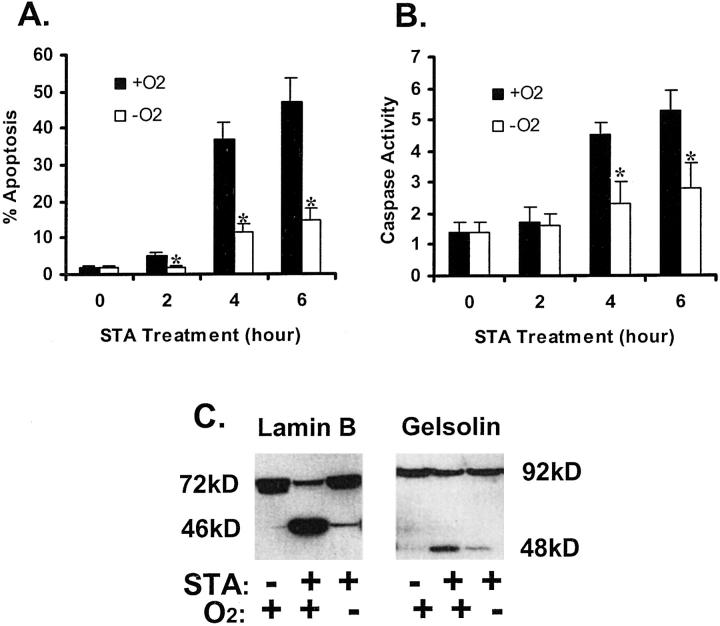
Figure 2.
Inhibition of staurosporine-induced apoptosis by hypoxia. A: % apoptosis estimated by cell morphology. B: Caspase activity. C: Proteolytic processing of lamin B and gelsolin. For measurements of apoptosis and caspase activity, cells were incubated for 0 to 6 hours with 1 μmol/L STA under normal 21% oxygen (+O2) or under severe hypoxia (−O2). Apoptotic cells were identified by cellular and nuclear morphology. Caspase activity was measured using the fluorogenic peptide substrate DEVD.AFC, as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as means ± SE (n = 4). *, significantly different from the results of the normoxic groups (P < 0.05). To analyze lamin B and gelsolin, cells were incubated for 4 hours with 1 μmol/L STA under normal 21% oxygen or under severe hypoxia. Control cells were incubated under normal oxygen without STA exposure. Whole cell lysates were collected for immunoblot analysis. STA-induced apoptotic morphology, caspase activation, and cleavage of lamin B and gelsolin under normal oxygen tensions; development of these apoptotic features was significantly diminished under hypoxia.