Fig. (1).
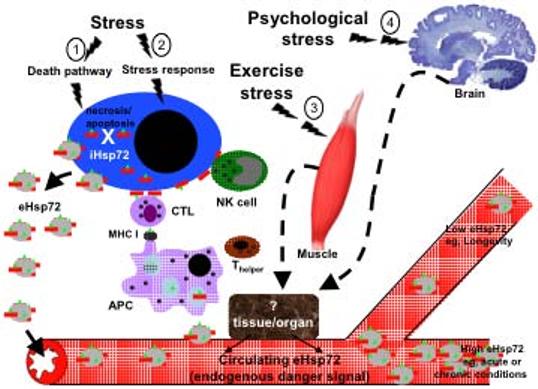
Model system for stress-induced release of Hsp72. Depending on the intensity and kind of stressful stimuli the following down stream effects can occur. 1) Non physiological stress (e.g., trauma or infection with lytic virus) will activate the cellular death pathway and result in intracellular (iHsp72) release into the circulation, refereed to as the passive release hypothesis. 2) Physiological, environmental, pathological (except infection with lytic virus) stress activates the stress response by triggering the trimerization and nuclear translocation of cytoplasmic HSF-1 and subsequent transcription of intracellular Hsp72 (iHsp72; red rod). The increased iHsp72 protects the cell from cell death under certain conditions. iHsp72 chaperones peptides (green triangle) and is expressed on the cell surface and released into the extracellular milieu within exosomes and free Hsp72. 3) Exercise stress or 4) Psychological stress stimulates the release of Hsp72 into the circulation via a still unknown tissue and/or organ. The released extracellular Hsp72 (eHsp72) make their way into the circulation where it acts as an endogenous danger signal. Antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages, B cells, dendritic cells, langerhans cells) bind eHsp72 to specific receptors and stimulates a signal transduction cascade that results in the initiation of an immune response characterized by the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, nitric oxide and costimulatory molecules. The eHsp72 is internalized by APC and the chaperoned peptide is processed and presented in the context of MHC class I to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), which lyse peptide bearing cells. Circulating eHsp72 induces NK cells migration and the expression of Hsp72 on the surface of stressed cells activates NK lytic functions. As an endogenous danger signal, circulating eHsp72 found in high concentrations is a good indicator of acute or chronic conditions, low eHsp72 concentrations have been linked to exceptional longevity.
