Figure 9. Effect of therapeutic coupled-cell tolerance to multiple myelin peptides on CNS peptide-specific T cell recall responses in established EAE.
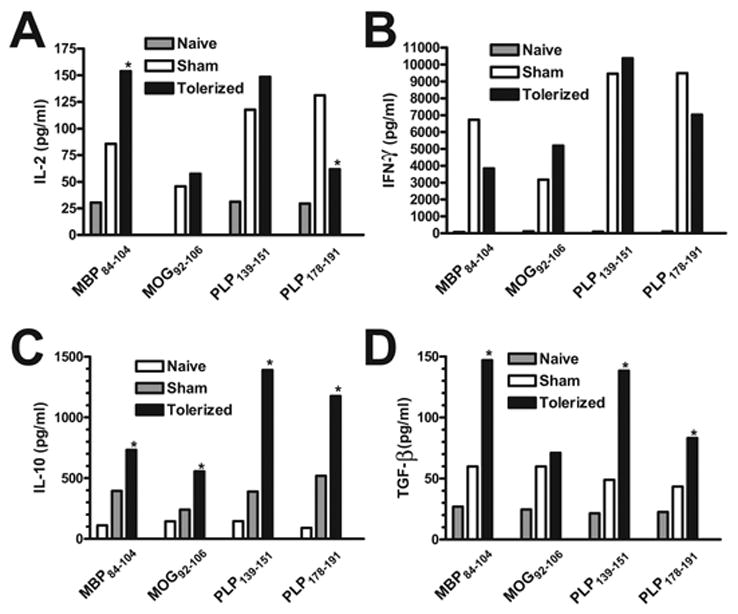
Twenty-six female SJL mice were primed s.c. with a cocktail of myelin peptides consisting of 25 μg PLP139–151, 50 μg PLP178–191, 100 μg MBP84–104, and 100 μg MOG92–106 and CFA on day 0. On day 15, at the peak of acute disease, mice were given 50×106 syngeneic splenocytes coupled to a myelin peptide cocktail consisting of PLP139–151, PLP178–191, MBP84–104, and MOG92–106 (Tolerized) or to a control peptide cocktail consisting of PLP56–70, OVA323–339, VP1233–250, and VP270–86 (Sham) i.v. On day 20, ten mice from each group were perfused, and spinal cords were harvested. Infiltrating leukocytes were isolated and single cell suspensions were incubated for 48 hr with the indicated antigens prior to measurement of IL-2 (A), IFN-γ (B) and IL-10 (C) levels via cytokine array analysis and TGF-β (D) levels via ELISA. Cytokine levels are reported as mean pg/ml and are representative of two separate experiments. *Responses significantly different than sham-tolerized controls, p < 0.05.
